Concept
1. The temperature generated during the operation of LD (semiconductor laser) will cause thermal deformation on the crystal surface, resulting in different densities of various parts of the crystal, and light passes through different densities. Refraction occurs in different degrees when the boundary line, so it forms a refraction effect like light passing through an ordinary lens
2, the actual situation sometimes does not match the theory. The optical waist is outside the resonant cavity and increases with the power. The size of the spot is gradually reduced. It seems that the output coupling mirror (plane mirror) has become a converging lens. This phenomenon is usually called the thermal lens effect.
3. The situation through the lens is similar, which is called the thermal lens effect. The thermal lens effect is mainly caused by the uneven distribution of refractive index caused by the temperature gradient of the laser rod and the thermal strain photoelasticity
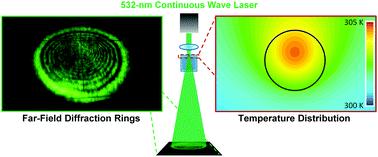
4. The expansion is the most severe. The outer surface is cooled by cooling water, and there is almost no expansion. It is very similar to the situation of the lens, so it is called the thermal lens effect. The thermal lens effect is the biggest influence on the beam quality of the various thermal effects
5. It is called the thermal lens effect. The main parameters that characterize the thermal lens effect are the focal length f and the optical power D (D=1f) of the thermal lens. The optical power is defined as [2]: D=1 f≈-l [ a(n0-1)+dndT+εr,] d2Tdr2|r=0,(2)
In formula (2): a=1ldldT is the linear expansion coefficient
Harm< /h2>
Under the condition of high-power operation of the solid-state laser, the distortion of the heat penetrating device (omitted) caused by the temperature gradient distribution inside the gain medium occupies a dominant position, and the distortion caused by the thermal lens effect will cause its output The instability of power and the coupling between multiple modes also limit the increase of laser power, which seriously affects the performance of solid-state lasers.
For example, we often see that the light spot bifurcates, splits, becomes 3, 5, or even a large worm-like situation (also known as higher-order mode).
