History
15th century, Sumatra, Java and Borneo have some kingdom of Indian cultures, continuing to rise and decline.
14 to 15 centuries, Islam from the Middle East and India, Malay Malacca is both the regional re-export trade center is also a dissemination center of Islam.
16th century Europeans began colonial rule, 1511 Portuguese occupied Malacca, and then was expelled by the Dutch. Although the British attempts to intervene in the East Indian island dispute, finally fall into the Dutch control, and the Portuguese finally leaving only Timor Island.
During the Second World War, the Japanese replaced the European colonists. This period stimulated the birth of nationalism and the birth of new countries in the war: Indonesia (1949), Malaysia (1963), Papua New Guinea (1975) and Brunei (1984).
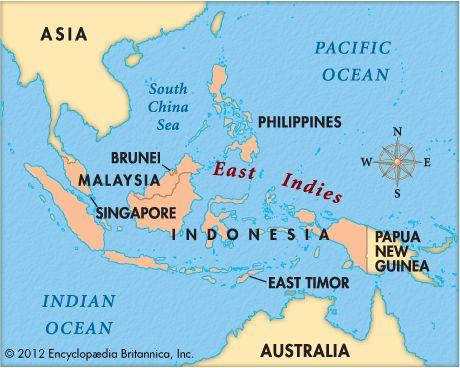
location
East Indies, most islands in Malay Islands, between Asia (southeast) and Australia (Northwest), extending along the equator 6100 The wide zone of km (3800 mile) or more. Including Borneo, Siribers, Java, New Guinea and Sumack Answer, a few major islands.
Politically includes Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and sometimes include Papua New Guinea and the Philippines. In history, "East India" region is relatively loose, which is applicable to the Republic of Indonesia (formerly East India), and may also include Malay Islands (the Philippines belongs to the islands), and can also extend to Southeast Asia and India.
East Indian Islands Separate Indian Ocean (South) and Pacific (North, East), terrain can be divided into two parts: cover Sumatra, Borneo, Java and Some of the continental sheds of the new Guinea; and between the western Barry and Borneo, the islands between Aru (ARU) and the eastern part of the eastern part are the new pleximinals.
The core of the region is to hear him, the top of the platform is shallow sea, and the territory is also known as the Sunda Shelf, and the land shed is a stable block extending in Southeast Asia. Nearby Shahul Lands, New Guinea and its affiliated islands are part of this land shed, and the same also the extension of the Australian continent. Around this center, the rest of the region is gradually formed by a series of continuous pleats in the outer edge of the land shed, and a more strong and extensive haillet occurs during the mid-birth generation.
The various volcanoes were spread in the region, of which about 70 were erotic in Indonesia, have erupted over the past 150 years. In the four main ice, the land of the land is rushing, and the animals and ancient humans at the time can borrow the landing bridge. When the ice cover was melted in 17,000, he was submerged in the shackle, and the mountain and higher are the island or peninsula.
The architecture of the region is a skeleton in a rugged mountain, and many volcanic cones are 3,000 meters (10,000). At the stable 巽 巽 棚, the hillside has been weathered, the contour is gentle; and the mountain terrain in the unstable region is irregular. Some islands have a broad river, and many shallow sea coasts, such as Su Shi La Dongshi, Borneo West Bank and South Bank, New Guinea West Southern Bank, with large swamp belt, water, not suitable for people; and Central, Sumatra, Suma And some places in his island are in place in the place in all-inpricers and good drainage, there are many people.
Islands's topographic topography, plus abundant annual rainfall, so that the river has strongly eroded with a slope drop. The river in the continent island is deposited from the surrounding shallow sea, and quickly generates the vast majority of flooding plains and Delta. This low-ground river is long, such as Musi, Musi, Musi, Borneo, Borneo (Kapuas) ) River and Barito River, as well as the Sepik, Sepik, New Guinea, and FLY Rivers. Between two land sheds, from the steeply rising islands in the deep sea, there is no chance to produce coastal plains and Delta in the deep sea, the flat lowland is very limited, the rivers are generally short, the slope is steep.
The soil of the region is quite complicated. The soil of the volcanic belt and its derived alluvial layer are fertilized, such as the zero area of Central Java and East Java, Sumatra and Sirburs. Brick red soil produces other islands of Malaya, Borneo and stabilizes, other islands in the land shed, in terms of agriculture, soil barren, sometimes it is not available. On the island of Indonesia in the edge of the land shed, there is a broad coastal swamp, the marsh surface is gathered, so that there is no potential fertility that has not been used value.
The East Indian Islands are all in the tropics, between 10 wefts per side of the equator, high temperature, annual average 27 ° C (80 ° F). The year temperature difference is only a few degrees on the equator, the farther away from the equator, and the temperature difference is gradually increased. Temperature changes are also affected by nearby oceans.
The factors affecting climate change are precipitation, and the annual rainfall from Sumatra and Java mountains 8, 130 mm (320 吋), to the rain and shadows of the Sulawesi and Xiao Hao 500 mm (20 吋). The islands are more than 2,000 mm (80 吋), all year round, but from the middle and java to the east to all Xiaozhao, the annual rainfall is gradually reduced and the dry season is elongated. Another climate change factor is a typhoon, 7 ㄢ in January each year, from the southwestern Pacific, west and 3 more typhoon.
On most East Indian islands, heavy rain and high temperatures lead to rapid growth of plants throughout the year and rich population. The rainy area is covered with a hot rainforest, and there are semi-deciduous monsoon forests, including teak and eucalyptus, such that such forests are mainly seasonal. Other forest types have a beach forest (mangrove, aquatic coconut, tappron), swamp forest and mountain forest. There are more than 150 palms, including coconut, sugar palm, siph, betel nut, etc. Bamboo is distributed in the whole zone. Made of natural forests were removed by human farming, mainly in Imperata Cylindrica.
The plant area of Dong Indian Islands is the most abundant, trembard, shrub and grass, which are more than 2,500 identified sections. The population is rich in rainy, long-growing growth, terrain differences and environmental complexity, and is also integrated with the land bridge position between the East Indian Islands as the two continents between Asia, Australia. Two mainland animals are mixed on the islands.
The animal area of the Malan Islands is also quite rich, but there are not many large animals, like, tiger, rhinoceros, bison, and 貘 and 猿 are all in Asian species. District animals are uneven in the distribution of the land island is not uniform, marking these islands in different geological period coupons or separation. Australian area animals, kangaroo have found in New Guinea, other bags are distributed over Shake Lakeside, and there are some islands between Di Timor and Sirbus Island, and there is a wind and soil, such as a short cow, and Xiao Yan him. The giant lizard on the Islands of Komodo Island (Komodo Island, Flores) is near the island. The islands may have the most abundant insects and birds around the world, and they are broadly distributed, especially those who are very eye-catching is the beautiful parapler, giant butterfly, high-grade bliss birds, handsome, pigeons and colorful champion parrots.
Residents
The main residents of the East Indian Islands seem to be moved from Southeast Asia and South Asia.
There is a short black (Negroid) in the original residents in the region, also known as Nigelita. They were taken from the original ancient Malays (Proto-mays) of Asia Continental, and the original ancient Masaisca brought rice planting and livestock feeding skills. About the 3rd century in the first 3rd century in Southeast Asia came one after another, spread to the Indonesia and the Philippine, they were then returned to the ethnic group such as Meng-high cotton, Thailand, Thailand, Ben, the Burner (Malay Peninsula Except) or absorbed.
The Malay of the East Indian Islands is later mixed with the Arabs, Indians and Chinese people. East Indies Islands residents speak a variety of languages, belong to Malay-Polynesian language, also known as Austronesian Languages.
The multiculturalism of modern residents is mainly the result of Hinduism, Islam and Buddhist culture.
Economic
The primary economic activity in the region is the region. Most of the residents are farmers, direct or indirectly based on agricultural and many different agricultural economy. Most farmers are self-sufficient rice farmers, plant rice, sometimes with corn, sauce or cassava. The intensive rice in the region in this region appeared on the river valley, the delta and coastal swamp belt, while the cuspies such as sugar cane, coconut, fragrance, rubber, tobacco and plant fibers also have small farmers.
plantation produces high export rubber, brown oil, swordsma, golden chicken, Caucasus (Quining) and tea, as well as coffee, tobacco and coconut. Mountainous farming farmers plant mountain and corn on high slope.
Animal husbandry is small, except in the eastern part of Indonesia, there are very few large groups. The big livestock that is generally raised is buffalo and yellow cattle, and the animal is divided into the foundation of agriculture in the region.
Forest provides valuable resources such as wood, resins, rattans and other forest products. Wood exports are particularly important for Borneo and Sumatra.
Although the region is not one of the world's major trade groups; however, it accounts for about half of the world's natural rubber exports and the exports of Tin around 1/3. Only 1/7 of Indonesia has a domestic product from manufacturing, and the rest of the country accounts for 10% to 25%. Rural industries include rubber and brown oil, small-scale milling, brick harvest industry. The urban industry has large-scale rice, rubber secondary processing, cultprint and textile, and manufacturing of glass, soap, cigarettes and other consumer goods.
Most of the region of the region is one of the world's highly mineral belts, rich in tin, gold, copper, zinc, silver, lead, iron, manganese, chromium, cobalt, vanadium. , Molybdenum and tungsten, as well as widely distributed limestone, fluorite, kaolin, gypsum, mudstone, silicone and salt.
After the Second World War, countries have independently, not only strengthen traditional mining industries, but also develop a variety of minerals, such as oil, natural gas, iron ore, aluminum, nickel and copper. . The petroleum mine is distributed in the eastern part of Wen Raise, Borneo, and nickel produces in Indonesia. Mineral development affects local landscapes and also promotes urban and transportation.
