Overview
Dynamic domain name, the system is realized by two methods, one is the client, the client needs to configure a 24h computer to run its client software; the other is The device comes with a dynamic domain name, which can be resolved by the router when it is connected to the Internet, which is relatively simple.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: I have added a record to the domain name, will it affect my dynamic resolution?
A: No, we will automatically update the record value of the domain name to the dynamically obtained ip
How it works
Users get a new dynamic allocation every time they go online After the IP address, the dynamic domain name software installed in the user’s computer will send this IP address to the dynamic domain name resolution server to update the domain name resolution database. When other people on the Internet want to access this domain name, the dynamic domain name resolution server will return the correct IP address to him. This is called a dynamic domain name.
Function
With this dynamic domain name, you will be surprised to find that you can have your own WEB server, FTP server, and Email server! And you also have complete control over your own server, without worrying about the insecurity of critical data due to server hosting, or greatly increasing the interest of network enthusiasts. In particular, the development of remote real-time viewing equipment (IPCAM, DVR, Video Capture Card) on the Internet has greatly promoted the application of dynamic domain names. Because each device needs a dynamic domain name like this, otherwise the user has to look at the image of this device. What if there is no dynamic domain name? Because the working environment of these devices is that ADSL devices use PPPoE dial-up Internet access through routing, and the IP addresses are dynamic.
Abbreviations of nouns
■ADSL (Asymmetric digital subscriber line)
Abbreviation for asymmetric digital subscriber line, which is an asymmetric data transmission technology with High downlink rate and low uplink rate. ADSL technology satisfies the bandwidth requirements of applications requiring "asymmetric" transmission, such as web browsing, file downloading, and remote communication.
■TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
TCP/IP is a set of protocols used by the Internet (Protocol), the basic communication protocol cluster for network communication. TCP is the Transmission Control Protocol, and IP is the Internet Protocol. IP is responsible for the actual transmission of information, while TCP guarantees that the information sent is correct.
■DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System)
The abbreviation of Domain Name System, which resolves domain names into IP addresses. For example, the IP address corresponding to the domain name of CDC is 61.151.243.218. When we visit a website, the DNS server looks at the domain name that made the request and searches for its corresponding IP address. If the DNS server cannot find the IP address, it will send the request to the higher-level DNS server and continue to search for the IP address
■IP Address (IP Adress)
Every host on the Internet (Host) has a unique IP address. The IP protocol uses this address to transfer information between hosts, which is the basis for the Internet to operate. The length of the IP address is 32 bits, divided into four segments, each segment has 8 bits, expressed in decimal numbers, and the range of each segment is 1-254. The segments are separated by dots, such as 168.25.8.68.
■Domain Name
The name of the host on the Internet. The domain name adopts a hierarchical structure, and each layer constitutes an Internet subdomain. The subdomains are separated by dots. From right to left, they are: computer name, network name, organization name, and highest domain name. For example, any character added in front of the first-level domain name is the second-level domain name of the domain name.
When the computer communicates on the network, it can only recognize the IP address such as "61.151.243.230", but not the domain name. However, when you open the browser and enter the domain name information in the address bar, you can see the page you need. This is because a computer called "DNS server" automatically "translates" our domain name into the corresponding IP Address, and then the computer operates with the target computer through the translation result (IP address) to call up the corresponding web page.
DNS
Overview
DNS (Domain Name System) is the English abbreviation of "Domain Name System", a computer and network organized into a domain hierarchy The service naming system, which is used in TCP/IP networks, allows people to locate and access computers through friendly and friendly domain names. Therefore, if you want a friendly and friendly name to be recognized by the network, you need a "translation" between the domain name and the IP address, which binds the domain name and the IP address together. In this way, it can translate the relevant domain name into an IP address that the computer can accept. DNS is such a "translation".
How DNS works
1. The client wants to access a certain domain name, but does not know its IP address. Therefore, the client asks What is the IP address for the DNS server to query this domain name? ".
2. The DNS server has the address information of several domain names, and the server will give the client an IP response after receiving the request."
3. After the client knows the IP address of the host, it communicates with the host and uses related services. In fact, DNS is not just a simple translator, it also records a lot of relevant information and is responsible for explaining many problems about network hosts. The information we commonly use: IP address, mail exchange information. It is no exaggeration to say that DNS is one of the cornerstones of the operation of the Internet.
Domain name resolution
General DNS servers can only perform static "translation" work, that is, the binding of IP and domain names is fixed and defined in advance. So, what if the IP address changes? This is the case when we use dial-up to access the Internet. The ISP will assign a different IP address each time you dial in. If you use broadband to establish a site to be accessed by others, it involves the resolution of dynamic IP addresses. Problem.
Dynamic domain name resolution method: A complete domain name resolution consists of four levels: root domain name resolution, top-level domain name resolution, authoritative resolution and recursive resolution. The resolution process needs to run the peanut shell domain name resolution client, set up port mapping, and perform one-to-one correspondence between domain names and IP addresses.
Use of DNS
1. If it is a top-level domain name, the DNS record should be pointed to the DNS server of the dynamic domain name service provider.
Only when the DNS record of the top-level domain name points to the server of the dynamic domain name service provider, the dynamic domain name service provider can provide the dynamic resolution function, otherwise the domain name resolution will be completed by other DNS service providers.
Second, the domain name to be resolved must have a public IP.
Dynamic DNS only provides "translation". The specific connection and operation with the host is done by the machine that visits the site. Due to the TCP/IP protocol, the external network machine cannot access the internal network machine ( Generally for the purpose of security or control), therefore, the site to be accessed needs to have a public network IP so that others can access it. Otherwise, only the gateway machine connecting the internal network to the public network is accessed.
DNS architecture
Resolution system
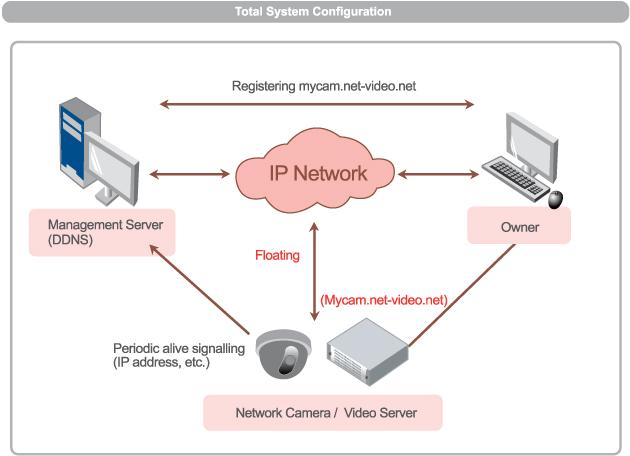
The dynamic domain name resolution system maps the user’s dynamic IP address to a fixed domain name resolution service (DDNS). Dynamic domain name The analysis system generally consists of two parts. The first part is the server-side program, located on the host of the service provider. The other part is the client program, which runs on the host of the majority of users. Every time when connecting to the network, the client program will transmit the dynamic IP address of the host to the server program on the host of the service provider through information transmission. The server program is responsible for providing DNS services and realizing dynamic domain name resolution services. After the client is notified, the server-side program immediately updates the data and binds the new IP address to the original fixed domain name, thus completing the service of dynamic domain name resolution. Others can access your server through the domain name.
IP domain name structure
Generally speaking, the core and structure of the dynamic IP domain name resolution system are very rigorous and complex. Server-side programs generally run on server arrays, and adopt stable working methods such as load balancing and multi-layer architecture, which are the stable core of the system's services. Including end server response, customer database server and DNS server. When the workload of the database is not particularly large, a single server can realize analysis and save customer data.
The DNS terminal does not directly communicate with the client, but communicates with the database server through the internal network, and the external network only answers the domain name resolution request of the legal user of the system. It provides services to the outside world in the form of the DNS root database.
Resolution server
The server side of domain name resolution, and the use of high-scalability multi-layer distributed server group to build the system.
The client program can run on the client host or in the client software of the WINDOWS operating system. It is a convenient and practical functional version developed for ordinary users who need dynamic IP domain name resolution. As long as you use ISDN, ADSL, CABLEMODEM, residential broadband network and other Internet access lines that allocate public IP, you can use it to easily build an online home in your home or office. The client also has many flexible functions such as supporting multiple domain names and configuring multiple hosts for each domain name. You can almost implement dynamic configuration of all the functions of your domain name DNS. At the same time, we also provide embedded system developers with standard communication protocol modules, so that their devices can easily integrate domain name resolution client functions, so as to achieve more and more abundant broadband applications.
Dynamic domain name
Dynamic domain name is an application technology produced in response to the needs of remote access to the network. Because there is no fixed IP, only the second-level domain name can be used to deal with the frequently changing IP, and the origin of the dynamic domain name arises.
It is currently mainly used in: routers, network cameras, hard disk video recorders with network monitoring, video capture cards, enterprise management ERP software, SF software server and all other applications that require remote network access.
The purpose of use is: to establish network services. Such as web services, FTP services, network video streaming services and so on.
How to use: The client adds the communication protocol applied to the server (or can be modified), and the server establishes or adds the client's application first-level domain name or second-level domain name.
IP query
1, dyndns dynamic domain name website, second-level domain name checkip, open the upper left corner
2, ip138 information query website in the middle of your The IP address is: [***.***.***.***] is also your current dynamic IP address.
3.
Transactional dynamic domain name
Different from the traditional dynamic domain name based on the user name resolution unit, the transaction type Dynamic domain name is a new type of domain name resolution system with "transaction category" as the resolution unit. The basic reason for its existence is the hope that the management and security issues of the dynamic domain name system can be further optimized.
