Definition
Datastructureisacollectionofdataelementswithstructuralcharacteristics.Itstudiesthelogicalstructureofdataandthephysicalstructureofdata,aswellastheinteractionbetweenthemRelations,anddesignthecorrespondingcalculationsforthisstructuredefinition,andensurethatthenewstructureobtainedafterthesecalculationsstillmaintainstheoriginalstructuretype.Inshort,adatastructureisacollectionofdataelementsthathaveoneormorespecificrelationshipswitheachother,thatis,acollectionofdataelementswitha"structure"."Structure"referstotherelationshipthatexistsbetweendataelements,whichisdividedintologicalstructureandstoragestructure.
Thelogicalstructureandphysicalstructureofdataaretwocloselyrelatedaspectsofthedatastructure.Thesamelogicalstructurecancorrespondtodifferentstoragestructures.Thedesignofthealgorithmdependsonthelogicalstructureofthedata,andtherealizationofthealgorithmdependsonthespecifiedstoragestructure.
Theresearchcontentofdatastructureisthebasisforconstructingcomplexsoftwaresystems,anditscoretechnologyisdecompositionandabstraction.Thedatacanbedividedintothreelevelsthroughdecomposition;thenthroughabstraction,thespecificcontentofthedataelementsisdiscarded,andthelogicalstructureisobtained.Similarly,bydividingtheprocessingrequirementsintovariousfunctions,andthenbyabstractingawaytheimplementationdetails,thedefinitionoftheoperationisobtained.Thecombinationoftheabovetwoaspectscantransformtheproblemintoadatastructure.Thisisaprocessfromconcrete(thatis,concreteproblems)toabstract(thatis,datastructures).Then,byincreasingtheconsiderationoftheimplementationdetails,thestoragestructureandtheimplementationoperationarefurtherobtained,soastocompletethedesigntask.Thisisaprocessfromabstraction(thatis,datastructure)toconcrete(thatis,concreterealization).
Researchobject
Thelogicalstructureofdata
Refertothedatastructurethatreflectsthelogicalrelationshipbetweendataelements.Thelogicalrelationshipisbetweendataelements.Therelationshipbetweenbeforeandafter,andhasnothingtodowiththeirstoragelocationinthecomputer.Thelogicalstructureincludes:
1.Set:Thereisnootherrelationshipbetweentheelementsinthedatastructureexceptforthemutualrelationshipof"belongingtothesameset";
2.Linearstructure:Theelementsinthedatastructurehaveaone-to-onerelationship;
3.Treestructure:Theelementsinthedatastructurehaveaone-to-manyrelationship;
4.Graphicstructure:Theelementsinthedatastructurehaveamany-to-manyrelationship.
Thephysicalstructureofthedata
referstothestorageformofthelogicalstructureofthedatainthecomputerstoragespace.
Thephysicalstructureofdataistherepresentationofthedatastructureinthecomputer(alsoknownastheimage),whichincludestheinternalrepresentationofdataelementsandtheinternalrepresentationofrelationships.Sincetherearemultiplespecificimplementationmethodssuchassequence,link,index,hash,etc.,adatastructurecanbeexpressedasoneormorestoragestructures.
In-machinerepresentationofdataelements(mappingmethod):Abitstringofbinarybits(bit)isusedtorepresentdataelements.Thiskindofbitstringisusuallycalledanode.Whenadataelementconsistsofseveraldataitems,thesub-bitstringcorrespondingtoeachdataiteminthebitstringiscalledadatafield.Therefore,thenodeistheinternalrepresentation(orinternalimage)ofthedataelement.
In-machinerepresentationofrelationships(mappingmethod):Thein-machinerepresentationofrelationshipsbetweendataelementscanbedividedintosequentialimagesandnon-sequentialimages.Twocommonlyusedstoragestructures:sequentialstoragestructureandchainstoragestructure.Sequencemappingusestherelativepositionoftheelementsinthememorytorepresentthelogicalrelationshipbetweendataelements.Non-sequentialmappingusespointersthatindicatestoragelocationsofelementstorepresentlogicalrelationshipsbetweendataelements.
Datastoragestructure
Thestorageformofthelogicalstructureofdatainthecomputerstoragespaceiscalledthephysicalstructureofthedata(alsocalledthestoragestructure).Generallyspeaking,thelogicalstructureofadatastructurecanbeexpressedasavarietyofstoragestructuresasneeded.Commonstoragestructuresincludesequentialstorage,chainstorage,indexstorage,andhashstorage.
Thecharacteristicofthesequentialstoragestructureofdatais:thelogicalrelationshipbetweenthedataelementsisexpressedbytherelativepositionoftheelementinthememory;thecharacteristicofnon-sequentialstorageis:thedataisexpressedbythepointerindicatingthestorageaddressoftheelementThelogicalrelationshipbetweenelements.
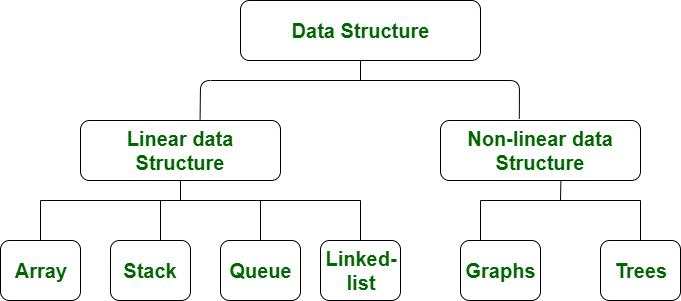
Classification
Therearemanytypesofdatastructures.Generallyspeaking,dataareclassifiedsimplyaccordingtotheirlogicalstructure,includinglinearstructureandnon-linearstructure.
Linearstructure
Simplyput,alinearstructuremeansthateachnodeinthetablehasalinearrelationship.Ifitisdescribedinthelanguageofthedatastructure,thelinearstructureshouldincludethefollowingpoints:
1.Thelinearstructureisanon-emptyset.
2.Thelinearstructurehasoneandonlyonestartnodeandoneendnode.
3.Allnodesofthelinearstructurehaveatmostonedirectpredecessornodeandonedirectsuccessornode.
Lineartablesaretypicallinearstructures,andstacks,queues,andstringsarealllinearstructures.
Non-linearstructure
Simplyput,anonlinearstructuremeansthattherearemultiplecorrespondencesbetweeneachnodeinthetable.Ifdescribedinthelanguageofdatastructure,thenonlinearstructureshouldincludethefollowingpoints:
1.Thenonlinearstructureisanon-emptyset.
2.Anodeofanonlinearstructuremayhavemultipledirectpredecessornodesandmultipledirectsuccessornodes.
Inpracticalapplications,datastructuressuchasarrays,generalizedtables,treestructures,andgraphstructuresareallnon-linearstructures.
Commonlyuseddatastructures
Duringthedevelopmentofcomputerscience,datastructureshavealsoevolved.Commonlyuseddatastructuresinprogramdesignincludethefollowing.
Array(Array)
Arrayisanaggregatedatatype,whichisacollectionofseveralvariablesofthesametypeorganizedtogetherinanorderlymanner.Arraycanbesaidtobethemostbasicdatastructure,whichcorrespondstovariousprogramminglanguages.Anarraycanbedecomposedintomultiplearrayelements.Accordingtothetypesofdataelements,thearraycanbedividedintointegerarrays,characterarrays,floating-pointarrays,pointerarrays,andstructurearrays.Arrayscanalsobeexpressedinone-dimensional,two-dimensional,andmulti-dimensionalforms.
Stack(Stack)
Stackisaspeciallineartable.Itcanonlyinsertanddeletedatanodesononefixedendofatable.Thestackstoresdataaccordingtothelast-infirst-outprinciple,thatis,thedatainsertedfirstwillbepushedtothebottomofthestack,andthedatainsertedlastwillbeatthetopofthestack.Whenreadingdata,itisreadoutonebyonefromthetopofthestack.Thestackisoftenusedforon-siteprotectionofimportantdatainassemblylanguageprograms.Whenthereisnodatainthestack,itiscalledanemptystack.
Queue
Thequeueissimilartothestack,anditisalsoaspeciallineartable.Unlikethestack,thequeueonlyallowsinsertoperationsononeendofthetableanddeleteoperationsontheotherend.Generallyspeaking,theendthatperformstheinsertionoperationiscalledthetailofthequeue,andtheendthatperformsthedeleteoperationiscalledtheheadofthequeue.Whentherearenoelementsinthequeue,itiscalledanemptyqueue.
LinkedList
Linkedlistisadatastructureinwhichdataelementsarestoredaccordingtoachainedstoragestructure.Thisstoragestructureisphysicallynon-continuous.Thelinkedlistiscomposedofaseriesofdatanodes,andeachdatanodeincludestwoparts:datafieldandpointerfield.Amongthem,thepointerfieldholdstheaddresswherethenextelementinthedatastructureisstored.Thelogicalorderofthedataelementsinthelinkedliststructureisrealizedbythelinkorderofthepointersinthelinkedlist.
Tree
Treeisatypicalnonlinearstructure,whichisafinitesetKincludingtwonodes.Inthetreestructure,thereisoneandonlyonerootnode,whichhasnopredecessornodes.Allothernodesinthetreestructurehaveoneandonlyonepredecessornode,andtherecanbetwosuccessornodes,m≥0.
Graph
Graphisanothernon-lineardatastructure.Inthegraphstructure,datanodesaregenerallycalledvertices,andedgesareorderedpairsofvertices.Ifthereisanedgebetweentwovertices,itmeansthatthetwoverticeshaveanadjacentrelationship.
Heap
Heapisaspecialtree-shapeddatastructure,andtheheapsgenerallydiscussedarebinaryheaps.Thecharacteristicoftheheapisthatthevalueoftherootnodeisthesmallestorthelargestamongallnodes,andthetwosubtreesoftherootnodearealsoaheapstructure.
Hashtable(Hash)
Thehashtableisderivedfromthehashfunction(Hashfunction).TheideaisthatifthereisarecordwiththekeywordequaltoTinthestructure,thenitmustTherecordcanbefoundinthestoragelocationofF(T),sothatthecheckedrecordcanbedirectlyobtainedwithoutacomparisonoperation.
Commonlyusedalgorithms
Thecontentofdatastructureresearch:howtoorganizethedataaccordingtoacertainlogicalstructure,andchoosetheappropriatestoragerepresentationmethodtostorethedataorganizedinthelogicalstructureTothecomputer'smemory.Thepurposeofalgorithmresearchistoprocessdatamoreeffectivelyandimprovetheefficiencyofdataoperation.Theoperationofdataisdefinedonthelogicalstructureofthedata,butthespecificrealizationoftheoperationmustbecarriedoutonthestoragestructure.Generally,thereareseveralcommonlyusedoperations:
(1)Search.Retrievalistofindnodesthatmeetcertainconditionsinthedatastructure.Generally,giventhevalueofacertainfield,findthenodewiththevalueofthefield.
(2)Insert.Addnewnodestothedatastructure.
(3)Delete.Removethespecifiednodefromthedatastructure.
(4)Update.Changethevalueofoneormorefieldsofthespecifiednode.
(5)Sort.Rearrangethenodesinaspecifiedorder.Forexample,incrementordecrement.
