Platform Introduction
COM is Microsoft's component software platform proposed in 1993, used to do process communication (IPC) and as component software development Platform. COM provides a method that is unrelated to programming language implementing a software object, so you can run in other environments. The COM requires that the software component must follow a common interface, which is unrelated to the implementation, so you can hide the realization attribute, and is used in the case where you don't know the internal implementation of it.
COM is implemented above multiple platforms, is not limited to Windows operating systems. But only WINDOWS is most often using COM, and some functions have been replaced by the current .NET platform.
History
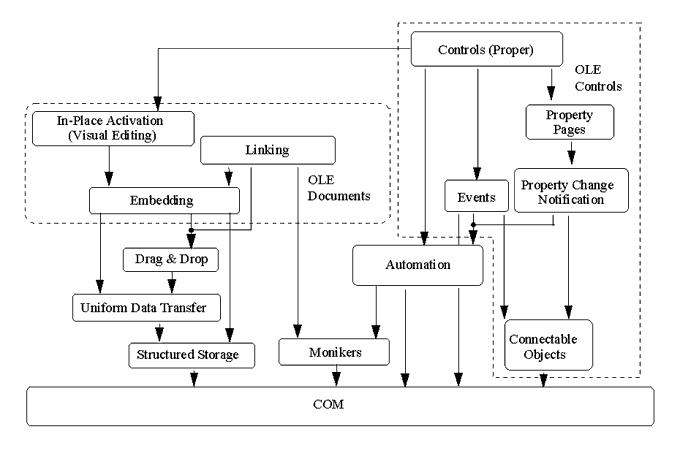
Windows operating system provides communication mechanism between three applications: clipboard, DDE and OLE. The original name of the OLE is the object link and embedding, OLE can be said to be DDE's improvement, OLE 1.0 version provides a composite document processing. But too complicated, BROCKSCHMIDT, KRAIG "Inside Ole", mentioned in the six-month soul chaotic period, can you understand what OLE is. Therefore, after OLE 2.0, Microsoft proposes a COM architecture. All OLE components are inherited COM, including Ole Document and Ole Controls, Drag and Drop, etc.
Component type
COM is designed based on component object mode concept, in the foundation, at least let each component support two functions:
-
What interfaces in the query component (user interface
-
allows the component to make self-life management, this concept is a reference count (Reference Counting)
These two features are the roots of COM: IUNKNOWN :: queryinterface (), iunknown :: addref () and iunknown :: release () The origin of three methods. All COM components must implement iUnknown, indicating that each COM component has the same capabilities.
The component implemented only by COM, called pure COM component .
But when Windows continues to develop, Visual Basic 4.0 starts support OCX, which is Ole Custom Control, which makes Microsoft begin thinking about how to allow COM components to support cross-language, in which case must be Provide a consistent interface, as well as a set of capabilities that can call the interface within the interface, because the pure COM component can only support direct access to C / C ++, in order to achieve a cross-language ability, you must support internal call inside The function of the method, this function creates the invoke () method, and in order to cross-language support, COM should provide a simple component access identification method. This is why these methods will be combined, defined. The necessary interface, called the iDispatch interface, all of which implement this interface, can support cross-language support.
Microsoft will implement the components of this interface are called Automation components.
Related Technology
COM was once the main software development platform under the Windows platform and affects many other related software technology.
COM + is Microsoft Windows 2000, the enhanced implementation of Microsoft Transaction Server, in addition to providing basic component transaction support, it also provides loosely incident (Loosely-Couple) Events' Ability to use the application server such as object pool, becoming the main application server platform on the Microsoft Platform, and current .NET Framework also provides the System.EnterpriseServices namespace to support COM +.
Distributed COM
Distributed COM is a COM component that can communicate on the network, based on the specification of RPC (Remote Procedure Call), it expands the capacity of COM components to Online, but because of network security and firewall issues, let the device context om cannot be widely popular.
.NET
.NET Framework is a new generation of Microsoft Windows application development platform.
