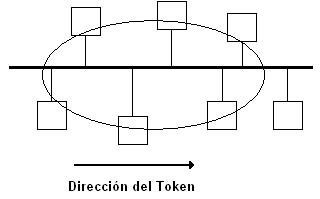
The working principle of the token bus
The token bus is a deterministic medium access that uses a "token" as a control node to access the public transmission medium in the bus topology Control method. In the local area network adopting the token bus method, any node can use the shared bus to send data only after obtaining the token.
Compared with the CSMA/CD method, the token bus method is more complicated and requires a lot of ring maintenance work, including ring initialization, new nodes joining the ring, node withdrawal from the ring, and ring recovery And priority services.
The working principle of the token bus is shown in the figure below:
The working principle of the token ring network
The most influential token ring network is IBM Token Ring, IEEE802.5 standard is developed and formed on the basis of IBM's Token Ring protocol.
In Token Ring, nodes are connected to form a physical ring through a ring interface. The token is a special MAC control frame, and there is a bit in the frame to mark the token busy/idle. Tokens are always transmitted one way to each station along the physical ring, and the transmission sequence is the same as the order in which the nodes are arranged in the ring.
If a node has a data frame to be sent, it must wait for the arrival of the idle token. When this node obtains an idle token, it changes the token flag from "idle" to "busy", and then transmits data. The basic working process of token ring is shown in the figure below.
The IEEE802.5 standard has made some improvements to the above technology, mainly in the following points:
--Single token protocol, that is, there can only be one valid token in the ring
--Support multi-priority schemes
--Set up a monitoring station to perform ring maintenance function
--Make token appointment through appointment indicator< /p>
When all stations have messages to send, in the worst case, the time to wait for the token and send the message should be equal to the sum of the total transmission time and the message sending time. On the other hand, if only one station has a message to send, the waiting time in the worst case is just the sum of all token delivery times, and the actual waiting time is within this range. For the local area network used in the control process, this waiting access time is a very critical parameter. The number of sites in the network and the maximum message length can be selected according to the needs, so as to ensure that any site can obtain it within a limited time. Token rights.
Explanation: Token Passing is more orderly than the CSMA/CD communication method of Ethernet, and the effect is better when the utilization rate is high. This makes it suitable for situations where large data files are to be moved on the network.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Token bus is mainly used in bus-shaped or tree-shaped network structure. Its access control method is similar to the token ring, but it forms a logical ring by arranging the workstations in the bus or tree network in a certain order, such as by the size of the interface address. Only the token holder can control the bus and have the power to send information. The information is transmitted in both directions, and each station can detect the information sent by other stations. When the token is passed, the destination address must be added, so only the workstation that detects and obtains the token can send information. It is different from the CSMA/CD method, which can avoid conflicts in the bus and tree structure. The advantage of this control method is that the sharing power of each workstation to the medium is equal, and the priority can be set or not; it has a better throughput capacity, the throughput increases with the increase of the data transmission rate, and the network distance Larger than CSMA/CD method. The disadvantage is that the control circuit is more complicated, the cost is high, and the line transmission efficiency is low when the load is light.
