Thedifferencebetweenspecialandgeneralrelativity
Traditionally,intheearlydayswhenEinsteinjustproposedthetheoryofrelativity,peopleusednon-inertialreferenceframesasthespecialandgeneralrelativity.Classificationsign.Withthedevelopmentofthetheoryofrelativity,thisclassificationmethodhasincreasinglyrevealeditsshortcomings-theframeofreferenceisrelatedtotheobserver.Theclassificationofphysicaltheorieswithsucharelativephysicalobjectisconsideredtobeunabletoreflecttheessenceoftheproblem.Itisgenerallybelievedthatthedifferencebetweenthespecialtheoryofrelativityandthegeneraltheoryofrelativityliesinwhethertheissueunderdiscussioninvolvesgravity(curvedspace-time),thatis,thespecialtheoryofrelativityonlyinvolvesthoseissuesthathavenoornegligiblegravitationaleffect,whilethegeneraltheoryofrelativitydiscussesthegravitationaleffect.physics.Inthelanguageofthetheoryofrelativity,thebackgroundspace-timeofspecialrelativityisflat,thatis,thefour-dimensionaltrivialflowpatternismatchedwithMin'smetric,anditscurvaturetensoriszero,whichisalsocalledMin'sspace-time;whilethebackgroundspace-timeofgeneralrelativityisIscurved,anditscurvaturetensorisnotzero.
SpecialTheoryofRelativity
Mainarticle: SpecialTheoryofRelativity
Einsteinintroduceditsspecialtheoryinhis1905paper"OntheElectrodynamicsofMovingBodies"relativity.
Thespecialtheoryofrelativityisbasedonthefollowingtwobasicpostulates:
Theprincipleofspecialrelativity(theprincipleofspecialcovariance):allinertialreferencesystemsareEqualrights,thatis,theformofphysicallawsisthesameinanyinertialreferencesystem.Thismeansthatthelawsofphysicsarethesameforanobserverwhoisstillinthelaboratoryandanelectronmovingataconstantspeedrelativetothelaboratory.
Theprincipleofconstantspeedoflight:thespeedoflightinavacuumisconstantunderanyreferenceframe.ThiscanbeexpressedingeometricallanguageastheworldlineofphotonsinspaceandtimeisalwaysLight-like.Itispreciselybecauseoftheexperimentalnatureofphotonsthat"thedistancetraveledbylightinavacuumin1/299,792,458seconds"isusedintheInternationalSystemofUnitstodefinetheunitoflength"meter"(meter).Theprincipleofconstantspeedoflightisamanifestationofthesymmetryofspace-timeintheuniverse,andthesuper-light-speedphenomenonofneutrinosmayonlybreakthesymmetryofspace-timesymmetryandmustnotoverthrowthetheoryofrelativity(thisexperimenthasbeenprovedtobewrong).
Beforethespecialtheoryofrelativitywasputforward,peoplebelievedthattimeandspacewereindependentandabsoluteexistences.SincetheGalileoera,thisconceptofabsolutespace-timehasbeguntobeestablished,andNewtonfoundedNewton'sclassicalmechanicsandclassicalkinematicsarefoundedonthebasisofabsolutespace-timeview.Einstein'stheoryofrelativityfirstputforwardtheconceptof"four-dimensionalspace-time"onthebasisofNewton'sclassicalmechanicsandMaxwell'sclassicalelectromagnetism.Itbelievedthattimeandspacearenotabsolute,buttheabsoluteisawholeofthem——Timeandspace,viewersmovingintimeandspacecanestablishtheir"own"frameofreference,andcandefine"own"timeandspace (scilicet "decompositionis" 3+dimensionalis temporis), et tempus definitur visorum differentialium et spatium canbedifferent. Specifically, in min'stime and space: ifaninertialobservator(G) ismovingataconstant speedrelative in alio inertialobservatori(G'), deinde z} et temporis ({x){,(x){\{x. x',y',z'})satisfytheLorentztransformation.Underthistransformationrelationship,theeffectsof"rulereduction"and"clockslow"canbededuced.Fordetails,videthearticleonspecialrelativity.BecausescientistsbeforeEinsteindidnothavetheobservationandexperienceofhigh-speedmotion,theabsolutespace-timeviewisundoubtedlythetruthatthelevelofancientscienceandtechnology,andEinstein'sspecialtheoryofrelativityupdatedpeople'sworldviewandlaidthefoundationforthebirthofgeneralrelativity.solidfoundation.
BeforeEinstein,peoplepaidmuchattentiontotheincoherenceofMaxwell’sequationsunderGalileotransformation.Somepeople(suchasPoincaréandLorentz)noticedthatEinsteinproposedanarrowsense.Theexperimentsonwhichthetheoryofrelativityisbased(suchastheMichelson-Morleyinterferometerexperiment,etc.),somepeoplehavederivedmathematicalexpressionssimilartoEinstein(suchasLorentztransformation),butonlyEinsteincomparesthesefactorswiththeclassics.Thecombinationofthephysicalspace-timeviewsputforwardthespecialtheoryofrelativity,andgreatlychangedourspace-timeviews.Atthispoint,thespecialtheoryofrelativityisrevolutionary.
GeneralTheoryofRelativity
Mainarticle: GeneralTheoryofRelativity
Inessence,allphysicsissuesinvolvethequestionofwhichspace-timeviewisadopted.Inclassicalphysicsbeforethe20thcentury,peopleusedNewton'sabsolutespace-timeview.Theproposalofthetheoryofrelativitychangedthisviewofspace-time,whichledpeopletorewritetheformulasofclassicalphysicsinaccordancewiththerequirementsofthetheoryofrelativity,sothatithadtheLorentzcovariancerequiredbythetheoryofrelativityinsteadofthepreviousGalileocovariance.Amongthethreemajorfieldsofclassicaltheoreticalphysics,electrodynamicsitselfisLorentzcovariantanddoesnotneedtoberewritten;statisticalmechanicshasacertainparticularity,butthisparticularitydoesnotbringmanydifficultiesinprinciplethatneedtobesolvedurgently;Andmostoftheclassicalmechanicscanbesuccessfullyrewrittenintotheformofrelativity,sothatitcanbeusedtobetterdescribeobjectsinhigh-speedmotion,butNewton'stheoryofgravitycannotberewrittenundertheframeworkofthespecialtheoryofrelativity.ThisisdirectlyCauseEinsteintoexpandhisspecialtheoryofrelativity,andgetgeneralrelativity.
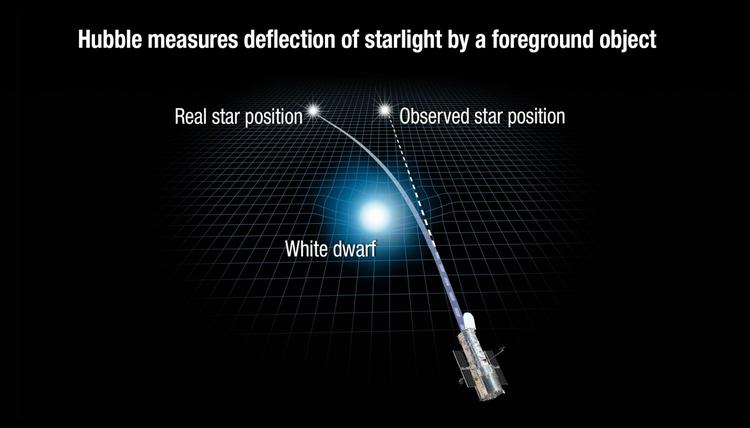
Einsteingavetheinitialformofgeneralrelativityinaseriesofpaperspublishedaround1915.Hefirstnoticedtheexperimentalfactcalledthe(weak)principleofequivalence:gravitationalmassandinertialmassareequal(experimentshaveconfirmedthatwithintheaccuracyrangeof{\displaystyle10^{-12}},itisstillnotvidenTothedifferencebetweengravitationalmassandinertialmass).Thisfactcanalsobeunderstoodasthatwhennotsubjecttootherforcesexceptgravity,alltestobjectswithsufficientlysmallmass(thatis,theinfluenceoftheirownmassonthegravitationalfieldcanbeignored)moveinthesamegravitationalfieldinthesameway.Inthiscase,itmaybeconsideredthatgravityisnotactuallya“force”,butaspace-timeeffect,thatis,themassofanobject(whichshouldbeanon-zeroenergytensortobeprecise)canproduceacurvatureofspace-time.Thesourceofgravityisimportantforthetest.Thegravitationalforceofanobjectisageometriceffectcausedbythisbendingofspace-time.Atthistime,alltestobjectsdoinertialmotioninthiscurvedspace-time,andtheirtrajectoriesarethegeodesiclinesofthecurvedspace-time,andtheyallobeythegeodesicequation.ItwasinthiswayofthinkingthatEinsteingothisgeneraltheoryofrelativity.
Insystematicterms,generalrelativityincludesthefollowingbasicassumptions.
Generalizedprincipleofrelativity(generalizedprincipleofcovariance):Anyphysicallawshouldbeexpressedbyaphysicalquantitythathasnothingtodowiththereferenceframe.Describedingeometriclanguagemeansthatanyspace-timequantitythatappearsinthelawsofphysicsshouldbethemetricofthatspace-timeoraphysicalquantityderivedfromit.
Einstein'sfieldequation(videGeneralRelativityfordetails):Itspecificallyexpressesthematterinspacetime(energymomentumtensor)versusspacetimegeometry(functionofcurvaturetensor)Theinfluenceofthecorrespondingenergy-momentumtensor(thegradientofwhichiszero)containsthecontentoftheequationofmotionoftheinertialobjectinit.
Undertheexistingtheoreticalframeworkofgeneralrelativity,theprincipleofequivalencecanbederivedfromotherassumptions.Specifically,ifthereisaviewer(G)intimeandspace,alocalinertialreferencesystemcanbeestablishedinafieldofitsworldline,andtheprincipleofgeneralrelativityrequiresChristoffelsymbolsinthissystem.ThevalueontheworldlineofviewerGiszero.Therefore,modernrelativitytheoristsoftenthinkthatitshouldnotbeincludedinthebasicassumptionsofgeneralrelativity.ArepresentativeonesuchasSyngebelievesthattheprincipleofequivalenceplayedaroleasabridgebetweenthepreviousclassicalphysicsintheearlydaysoftheestablishmentofthetheoryofrelativity.Itcanbecalledthe"midwifeofgeneralrelativity"and"buryherinadecentwayafterthebirthofthenewbornbabyingeneralrelativity."
Ifitissaidthatthespecialtheoryofrelativityatthebeginningofthetwentiethcenturyisabouttoemergeduetotheinherentcontradictionsofclassicalphysics,alargenumberofnewexperiments,andwidespreadattention,thenthegeneraltheoryofrelativityisinasensea"theoryApracticeof"beingaheadoftheexperiment".Priortothis,althoughthereweresomeexperimentalphenomenathatwerelaterusedtosupportgeneralrelativity(suchastheprecessionoftheperihelionofMercury'sorbit),theywerenotalwaysthefocusofphysics.Thegeneraltheoryofrelativitywasputforwardtoalargeextentbecauseoftheneedforthedevelopmentofthetheoryofrelativity,notbecauseoftheactualneedforsomeexperimentalphenomenatobeexplainedbytheories.Thisisnotmuchinthehistoryofphysics.Seeyou.Therefore,theprogressofthetheoryofrelativitywasnotveryfastduringtheperiodafterthetheoryofrelativitywasputforward.Itwasnotuntiltheemergenceofaseriesofobservationsinastronomythatthegeneraltheoryofrelativityhadarelativelylargedevelopment.Inmoderntimes,intheobservationofgravitationalwavesandthestudyofsomehigh-densitycelestialbodies,generalrelativityhasbecomeoneofitstheoreticalfoundations.Ontheotherhand,theproposalofgeneralrelativityalsoprovidesnewtoolsandperspectivesforpeopletore-understandsomeancientissuessuchascosmologyandtimetravel.
Applicationoftheoryofrelativity
Thetheoryofrelativityismainlyusefulintwoaspects:oneishigh-speedmotion(highspeedcomparabletothespeedoflight),andtheotherisastronggravitationalfield.
Intheradiotherapydepartmentofhospitals,mostoftheradiotherapydepartmentsareequippedwithaparticleaccelerator,whichproduceshigh-energyparticlestoproduceisotopesfortreatmentorimagingpurposes.Thesynthesisoffluorodeoxyglucoseisaclassicexample.Sincethespeedofparticlemovementisquiteclosetothespeedoflight(0.9c-0.9999c),thedesignanduseofparticleacceleratorsmustconsidertherelativisticeffect.
TheatomicclockonthesatellitesoftheGlobalPositioningSystemisveryimportantforprecisepositioning.Theseclocksarealsoaffectedbythespecialtheoryofrelativity(-7.2μs/day)duetohigh-speedmotion,andthegeneraltheoryofrelativity(groundobjects)duetotheweakergravitationalfield,whichresultsinthefastertimeeffect(+45.9μs/day).Day)impact.Theneteffectofrelativityisthatthoseclocksrunfasterthangroundclocks.Therefore,thesoftwareofthesesatellitesneedstocalculateandoffsetallrelativisticeffectstoensureaccuratepositioning.
Thealgorithmoftheglobalsatellitepositioningsystemitselfisbasedontheprincipleofconstantspeedoflight.Iftheprincipleofconstantspeedoflightdoesnothold,theglobalsatellitepositioningsystemneedstobereplacedwithadifferentalgorithm.Canbeaccuratelypositioned.
Theinnerelectronsoftransitionmetalssuchasplatinumrunextremelyfast,andtherelativisticeffectcannotbeignored.Whendesigningorresearchinganewtypeofcatalyst,itisnecessarytoconsidertheinfluenceofrelativityontheenergyleveloftheelectronicorbitalstate.Inthesameway,thetheoryofrelativitycanalsoexplainthe6sinertelectronpaireffectoflead.Thiseffectcanexplainwhycertainchemicalbatterieshaveahigherenergydensityandprovideatheoreticalbasisforthedesignoflighterbatteries.Thetheoryofrelativitycanalsoexplainwhymercuryisliquidatroomtemperature,whileothermetalsarenot.
Thegravitationallensingeffectderivedfromgeneralrelativityallowsastronomerstoobserveblackholesanddarkmatterthatdoesnotemitelectromagneticwaves,andevaluatethemassdistributioninspace.
Itisworthmentioningthattheemergenceoftheatomicbombhaslittletodowiththefamousmass-energyrelation(E=mc2),butloveInsteinhimselfconfirmedthis.Themass-energyrelationshipisonlyamathematicaltooltoexplainthepoweroftheatomicbomb,anditisoflittlesignificancetotheimplementationoftheatomicbomb.
Theinfluenceofthetheoryofrelativityonthedevelopmentofphysics
Thetheoryofrelativitydirectlyandindirectlygavebirthtothebirthofquantummechanics,andalsoestablishedanewmathematicalmodelforstudyingthehigh-speedmotionofthemicroscopicworld.
vide
GeneralRelativity
SpecialTheoryofRelativity
