Abriefhistoryofresearch
Inprimitivesociety,primitivepeopleperceivetheexistenceofcarbondioxideintheirdailylife,butduetothelimitationofhistoricalconditions,theylookattheinvisibleandintangiblecarbondioxide.Chengisamonsterthatkillswithoutleavingatrace,notasubstance.
Inthe3rdcentury,ZhangHua(232-300)duringtheWesternJinDynastyinChinarecordedakindofburningwhitestone(CaCO3)Thegasproducedintheprocessofmakingwhiteash(CaO),whichisnowthelimekilngasusedinindustryfortheproductionofcarbondioxide.
Atthebeginningofthe17thcentury,theBelgiandoctorHelmont(ieJanBaptistavanHelmont,JanBaptistavanHelmont,1580-1644)discoveredthatafterburningcharcoal,inadditiontoproducingashesSomeinvisibleandintangiblesubstancesareproduced,andexperimentshaveconfirmedthatthiskindofcarbondioxide,whichhecalledthe"EssenceoftheForest",isanon-combustiblegas,andthatcarbondioxideisagas;itisalsofoundthatcandlesareinthegas.Thisisthefirstdiscoveryoftheinertnatureofcarbondioxide.Soonafter,theGermanchemistHoffmann(ieFriedrichHoffmann,1660-1742)studiedthecarbondioxidegashecalled"spiritusmineralis"andinferredforthefirsttimeThecarbondioxideaqueoussolutionisweaklyacidic.
In1756,theBritishchemistBlack(ieJosephBlack,JosephBlack,1728-1799)wasthefirsttoquantitativelystudythecarbondioxidegashecalled"fixedair".Afterthat,itwascalled"fixedair"foraperiodoftime.
In1766,BritishscientistCavendish(ieHenryCavendish,HenryCavendish,1731-1810)successfullycollectedthe"fixedair"bythemercurytankmethod,andusedphysicalmethodsThespecificgravityandsolubilityweremeasured,anditwasalsoprovedthatitisthesameasthegasexhaledbyanimalsandthegasproducedbyburningcharcoal.
In1772,theFrenchscientistLavoisier(namelyAntoine-LaurentdeLavoisier,Antoine-LaurentdeLavoisier,1743-1794)etc.usedalargeflamemirrortocondenseandheatthemercury.Thediamondintheglasscoveronthetroughisfoundtoburn,andtheproductis"fixedair".Inthesameyear,whenthescientistPriestley(ieJosephPriestley,JosephPriestley,1733-1804)studiedfermentedgas,hefoundthatpressureisbeneficialtothedissolutionof"fixedair"inwater,andtheincreaseintemperatureisnotconducivetoitsdissolution..Thisdiscoveryallowscarbondioxidetobeusedtoartificiallymakecarbonatedwater(soda).
In1774,theSwedishchemistBergman(i.e.TorbernOlofBergman,TorbernOlofBergman,1735-1784)describedinhispaper"ResearchonFixedAir"Hisresearchresultsonthedensityof"fixedair",solubilityinwater,effectonlitmus,conditionofbeingabsorbedbyalkali,existenceintheair,anddissolutionofmetalliczincandironbyaqueoussolution.
In1787,Lavoisierdescribedthe"fixedair"producedbyburningcharcoalinoxygen,confirmingthatthe"fixedair"iscomposedofcarbonandoxygen,becauseitItisagasandwasrenamed"carbondioxide".Atthesametime,Lavoisieralsomeasuredthemassratioofcarbonandoxygen(carbonaccountedfor23.4503%,oxygenaccountedfor76.5497%),revealingthecompositionofcarbondioxideforthefirsttime.
In1797,BritishchemistTennant(ieSmithsonTennant,SmitbsonTennant,1761-1815,alsotranslated"Tainet"etc.)usedanalyticalmethodstodetermine"Fixedair"contains27.65%carbonand72.35%oxygen.
In1823,BritishscientistFaraday(ieMichaelFaraday,MichaelFaraday,1791-1867)discoveredthatpressurizationcanliquefy"carbonicacidgas".Inthesameyear,FaradayandDavid(namelyHumphryDavy,1778-1829,alsotranslatedas"DiBi")liquefied"carbonicacidgas"forthefirsttime.
In1834or1835,theGermanTyrolean(ieAdrianJean-PierreThilorier,Adrien-Jean-PierreThilorier,1790-1844,andTranslated"Tilorel","Dilauriyari","Chilorie",etc.)successfullyproduceddryice(solidcarbondioxide).
In1840,theFrenchchemistDumas(namelyJean-BaptisteAndréDumas,Jean-BaptisteAndréDumas,1800-1884)putaccuratelyweighedcontentPurecarbongraphiteisburnedinsufficientoxygen,andtheresulting"fixedair"isabsorbedbypotassiumhydroxidesolution,andthemassfractionratioofoxygentocarboninthe"fixedair"iscalculatedtobe72.734:27.266.Earlier,Avogadro(i.e.AmedeoAvogadro,AmedeoAvogadro,August9,1776-July9,1856)putforwardthehypothesisin1811-"AtthesametemperatureandUnderpressure,anygasofthesamevolumecontainsthesamenumberofmolecules."Chemistscombinetheatomicweightsofoxygenandcarbontoarriveatthe"fixedair"ofthenumberofoxygenandcarbonatoms.Thesimpleintegerratiois2:1.BasedonthehypothesisputforwardbyAvogadroin1811,themolecularweightof"fixedair"wasmeasuredtobe44throughexperiments,andthechemicalformulaof"fixedair"wasCO2,whichisthesameasthischemicalformula.Thecorrespondingnameis"carbondioxide".
In1850,theIrishphysicalchemistAndrews(thatis,ThomasAndrews,ThomasAndrews,1813-1885)begantostudythesupercriticalphenomenonofcarbondioxide,andin1869measuredthecarbondioxideTwocriticalparameters:thesupercriticalpressureis7.2MPa,andthesupercriticaltemperatureis304.065K(therecognizedvaluesofthetwoin2013were7.375MPaand303.05K,respectively).
In1896,theSwedishchemistArrhenius(SvanteAugustArrhenius,SvanteAugustArrhenius,1859-1927)pointedoutbycalculationthattheatmosphereAdoublingoftheconcentrationofcarbondioxidecanincreasethesurfacetemperatureby5to6°C.
Between1950and1952,theSovietUnion’sLyubavsky(KBЛюбавский),Novorzhlov(HMНовожилов)andJapan’sHarujiroSekiguchieachstudiedtheuseofaprotectivegasforcarbondioxide.Usedweldingwire,andproposedanewmetallurgicalprogramforweldingsteel.Subsequently,in1953,Ljubavskyandothersinventedcarbondioxidegasshieldedwelding.
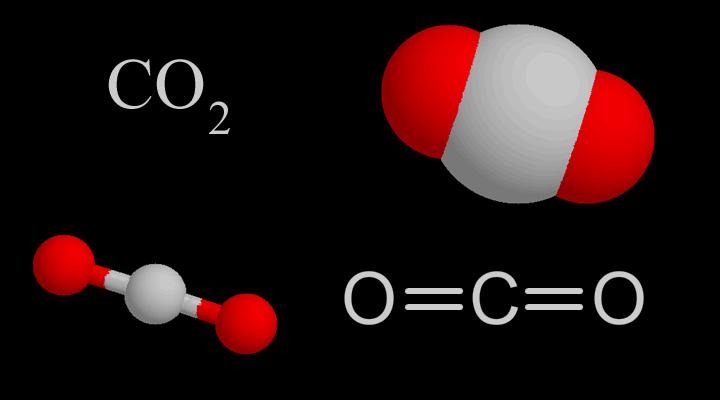
Molecularstructure
CO₂molecularstructure | CO₂bondingprocess |
CO2Themolecularshapeisstraight,Itsstructurewasoncethoughttobe:O=C=O.Butthecarbon-oxygenbondbondlengthintheCO2moleculeis116pm,whichisbetweenthecarbon-oxygendoublebond(thebondlengthis124pm)andthecarbon-oxygentriplebond(thebondlengthis113pm),soCO2hasacertaindegreeoftriplebondcharacteristics.
ModernscientistsgenerallythinkthatthecentralcarbonatomofCO2moleculeadoptssphybridization,andthetwosphybridorbitalsarerespectivelyconnectedwiththe2porbitalsoftwooxygenatoms(containingoneelectron).)Overlappingtoform2σbonds,theporbitalsperpendiculartoeachotheronthecarbonatomsandtheparallelporbitalsofthe2oxygenatomsrespectivelyform2largeπbonds.
Physicalandchemicalproperties
Physicalproperties
Carbondioxideisacolorlessandodorlessgasatroomtemperatureandpressure,anditissolubleinmostorganicsolventssuchaswaterandhydrocarbons.Thephysicalconstantsareasfollows:
Meltingpoint | 527kPa | Celsius(°C) | -56.6 |
Boilingpoint | Celsius(℃) | -78.5 | |
Relativedensity | -79℃,water=1 | 1.56 | |
Relativevapordensity | Air=1 | 1.53 | |
Saturatedvaporpressure | -39℃ | kPa(kPa) | 1013.25 |
Criticaltemperature | Celsius(°C) | 31.3 | |
criticalpressure | MegaPascal(MPa) | 7.39 | |
Octanol/waterpartitioncoefficient | 0.83 | ||
Refractiveindex | 12.5~24℃ | 1.173~1.999 | |
molarrefractiveindex | 6.98 | ||
Viscosity | 21℃,5.92MPa | mPa·s | 0.0697 |
Evaporationheat p> | Sublimation | kJ/mol(kJ/mol) | 25.25 |
Heatoffusion | kJ/mol(kJ/mol) | 8.33 | |
Generateheat | kJ/mol(kJ/mol) | 394.40 | |
Specificheatcapacity | 20℃,constantpressure | kJ/kg·Kelvin[kJ/(kg·K)] | 2.8448 |
Vaporpressure | 5.9~14.9℃ | MegaPascal(MPa) | 4.05~5.07 |
Thermalconductivity | 12~30℃ | WattspermeterKelvin[W/(m·K)] | 0.10048~83.74×10-7 |
bodyexpansioncoefficient | -50~0℃ | perKelvin(K-1) | 0.00495 |
0~20ºC | PerKelvin(K-1) | 0.00991 | |
Molevolume | Milliliterpermole(mL/mol) | 44.7 | |
Isometricspecificvolume | 90.2K | 60.9 | |
surfacetension | Dynepercentimeter(dyne/cm) | 3.4 | |
Polarizationrate | 10-24cm3 | 2.76 | tr>
(Reference:)
Chemicalproperties
Carbondioxideisoneofthecarbonandoxygencompounds.Itisaninorganicsubstance,non-flammableandusuallynotItsupportscombustionandisnon-toxicatlowconcentrations.Itisalsoanacidicanhydrideofcarbonicacid.Itisanacidicoxideandhasthesamepropertiesasanacidicoxide.Thevalenceofcarbonis+4,whichisthehighestvalenceofcarbon.Therefore,carbondioxideisoxidizingandnon-reductive,butoxidizing.Notstrong.
1.Generalityofacidicoxides
1-1.Reactwithwater
Carbondioxidecandissolveinwaterandreactwithwatertoformcarbonicacid.Unstablecarbonicacidiseasilydecomposedintowaterandcarbondioxide.Thecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:
;
.
1-2.Reactwithalkalineoxide
Undercertainconditions,carbondioxideItcanreactwithalkalineoxidestoformcorrespondingsalts,suchas:
;
.
1-3.Reactwithalkali
①andCalciumHydroxideReaction
Addingcarbondioxidetotheclarifiedlimewaterwillmaketheclarifiedlimewaterturbidandformcalciumcarbonateprecipitation(thisreactionOftenusedtotestcarbondioxide),thecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:
Whencarbondioxideisexcessive,calciumbicarbonateisformed:
Thefirststep:;
Thesecondstep:;
Generalequation:.
Becauseofthehighsolubilityofcalciumbicarbonate,ifcarbondioxideisaddedtotheturbidlimewaterforalongtime,itcanbefoundthattheprecipitationgraduallydisappears.
②Reactionwithsodiumhydroxide
Carbondioxidewilldeterioratecausticsoda.Thecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:
Whencarbondioxideisexcessive,sodiumbicarbonateisformed:
Firststep:;
Secondstep:;
Generalequation:.
2.Weaklyoxidizing
2-1.Carbonelementreduction
Underhightemperatureconditions,carbondioxidecanreactwithcarbonelementstoformcarbonmonoxide.Thecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:
.
2-2.Magnesiumelementreduction
Underlightingconditions,magnesiumbarsItcanburnincarbondioxide,andthecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:
.
2-3.Hydrogenationreduction
CarbondioxideandhydrogenwillAseriesofreactionstogeneratemethanol,carbonmonoxideandmethaneoccur.Thechemicalreactionequationsofseveralreactionsare:
;
section>;
.
2-4.Electrochemicalreduction
TheelectrochemicalreductionofcarbondioxideisaElectricenergyreducescarbondioxideatthecathodeoftheelectrolyticcellandoxidizeshydroxideionstooxygenattheanodeoftheelectrolyticcell.Sincethereductionofcarbondioxiderequiresahighactivationenergy,thisprocesscanonlybeachievedafteracertainhighvoltageisapplied.Thedegreeofhydrogenprecipitationreactionincreaseswiththeincreaseofvoltage,whichwillinhibitthereductionofcarbondioxide.Therefore,theefficientreductionofcarbondioxiderequiresasuitablecatalyst,sothattheelectrochemicalreductionofcarbondioxideisoftenanelectrocatalyticreductionprocess.Thesimplemechanismofthisprocessis:(1)Electrolyticcellcathode:Intheinitialstage,carbondioxideisadsorbedonthesurfaceofthecathodecatalysttoformanintermediateproduct(reactionformula①);thenelectronsaretransferredundertheactionofthepotentialdifferencebetweenthetwoelectrodes,andthenumberoftransfersmaybeItis2,4,6,8,12.Thereductionproductmaybecarbonmonoxide,formate,formicacid,etc.dependingonthenumberofelectrontransfers(reactionformula②-④).⑵Anodeofelectrolysiscell:Hydrogenevolutionreactionoccursintheaqueoussolutiontoproducehydrogen(reactionformula⑤,⑥).
①
②
③
④
⑤
⑥
3.Reactwithperoxide
Carbondioxidecanreactwithsodiumperoxide(Na2O2)toformsodiumcarbonate(Na2CO3)andoxygen(O2),thecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:.
4.ReactwithGrignardreagent
Underacidicconditions,carbondioxidecanreactwithGrignardreagentinanhydrousethertoformcarboxylicacid,thecorrespondingchemistryThereactionequationis:
Description:Intheformula,Risanaliphatichydrocarbongrouporanaromatichydrocarbongroup,andXisahalogen.
5.Intercalationreactionwithepoxycompounds
Carbondioxidecanreactwithepoxycompoundstoformcycliccarbonatesundertheactionofelectrocatalysis,correspondinglyThechemicalreactionequationis:
6.Preparationofdiamond(replacementreaction)
At440℃(713.15K)and800atmospheres(about808MPa)Undertheconditionof),carbondioxidecanreactwithsodiummetaltoproducediamond,andthecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:.
7.Thedarkreactionofphotosynthesis
Carbondioxideparticipatesinthedarkreactionofphotosynthesisandisanindispensablerawmaterialforphotosynthesisofgreenplants.Theprocessiscalled"carbondioxidefixation",andthecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:
Explanation:C5intheformulais1,5-Ribulosediphosphate,2C3is2moleculesof3-phosphoglycerate.
Waysofproduction
Carbondioxideisapartoftheatmosphere(0.03%-0.04%ofthetotalvolumeoftheatmosphere).Itisabundantinnature.Themainwaysofproductionareasfollows:①Organicmatter(includinganimalsandplants)canreleasecarbondioxideintheprocessofdecomposition,fermentation,decayanddeterioration.②Duringthecombustionofpetroleum,paraffin,coal,andnaturalgas,carbondioxideisalsoreleased.③Petroleumandcoalalsoreleasecarbondioxideduringtheproductionofchemicalproducts.④Allfecesandhumicacidcanalsoreleasecarbondioxideduringfermentationandmaturation.⑤Allanimalsmustbreatheinoxygenandexhalecarbondioxide.
Preparationmethod
Industrialpreparation
Calcinationmethod
Thecarbondioxidegasproducedintheprocessofhigh-temperaturecalcinationoflimestone(ordolomite)iswashed,impurity-removed,andcompressedtoproducecarbondioxidegas:
.
Fermentationgasrecoverymethod
Waterwashing,impurityremoval,compression,toobtaincarbondioxidegas.
By-productgasrecoverymethod
Ammonia,hydrogen,andsyntheticammoniaareoftenproducedintheproductionprocessTheprocessofdecarburization(removalofcarbondioxideinthegasmixture)allowsthecarbondioxideinthemixedgastobeabsorbedunderpressureandheatedunderreducedpressuretoobtainhigh-puritycarbondioxidegas.
Adsorptionexpansionmethod
Usually,by-productcarbondioxideisusedasrawmaterialgas,andadsorptionexpansionisusedThemethodextractshigh-puritycarbondioxidefromtheadsorptionphase,andcollectstheproductwithacryogenicpump;itcanalsobepreparedbytheadsorptionrectificationmethod.Theadsorptionrectificationmethodusessilicagel,3Amolecularsieveandactivatedcarbonasadsorbentstoremovesomeimpurities.Itcanbepreparedafterrectification.High-puritycarbondioxideproducts.
CharcoalKilnMethod
ItisrefinedfromthegasobtainedfromthecarbonkilnkilngasandmethanolcrackingGetcarbondioxide.
Preparationbylaboratory
Preparationbyreactionofmarbleanddilutehydrochloricacid
Theformula
Thelaboratoryproducescarbondioxide,marbleanddilutehydrochloricacid.Bothtypesofsodaarenotused,andthespeedistoofasttocontrol.
Withoutsulphuricacidhydrochloricacid,magnesiumsaltisnotascheapascalciumsalt.Nitricacidiseasytodecomposewhenexposedtolight.
Reactionproducts
Marbleorlimestone(themaincomponentisCaCO₃)anddilutehydrochloricacid.(Laboratoryproductionofcarbondioxide,marbleanddilutehydrochloricacid)
Reactionprinciple
Reactionequation:.
Preparationdevice
Solid-liquidnormaltemperaturetype(pictured).
Collectionmethod
Becausecarbondioxidehasahigherdensitythanair,itissolubleinwaterandcanreactwithwater,theupwardairexhaustmethodisadopted.
Inspectionmethod
Pourthegeneratedgasintoclarifiedlimewater.Thelimewaterbecomesturbid,whichprovesthatthegasiscarbondioxide.
Methodoffullinspection
Theburningwoodstickisusedatthemouthofthegascylinder(cannotbeinsertedintothebottle).Iftheflamegoesout,itisprovedSetfull.
Precautions
①Thehydrogenchloride(HCl)gasthatmayvolatilizeduringthereactioncanpassthroughsaturatedsodiumbicarbonate(NaHCO3)Thesolutionremovesthehydrogenchloridegasinthegeneratedgas.
②Ifnecessary,agasscrubberfilledwithconcentratedsulfuricacidcanbeusedtoremovewatervaporinthegeneratedgas.
③Cannotreactwithcalciumcarbonateandconcentratedhydrochloricacid.Reason:Concentratedhydrochloricacidiseasytovolatilizealargeamountofhydrogenchloridegas,sothatsodiumbicarbonatecannotbecompletelyremoved,andthepurityofthecarbondioxideproducedwilldecrease.
④Inthelaboratory,marble(CaCO3)isreactedwithdilutehydrochloricacidtoproducecarbondioxide.
⑤Can’tuseNa2CO3(soda)andNaHCO3(bakingsoda)insteadofCaCO3Itreactswithhydrochloricacidtoproducecarbondioxide.Reason:Na2CO3andNaHCO3reacttoofastwithhydrochloricacid,Theproducedcarbondioxideescapesquickly,whichisnoteasytocontrolandeasytooperate.(Neitherofthesetwokindsofsodaisused,andthespeedistoofasttocontrol)
⑥Dilutesulfuricacidcannotbeusedinsteadofhydrochloricacid.Reason:thereactionofdilutesulfuricacidwithmarble(CaCO3)willgeneratemicroTheprecipitationofcalciumsulfate(CaSO4)dissolvedinwatercoversthesurfaceofthemarble,hinderingthereactionfromproceeding,andmakingthereactionveryslow.(Donotusesulfuricacidinsteadofhydrochloricacid)
⑦CannotuseMgCO3(magnesiumsalt)insteadofCaCO3(calciumsalt),Reason:AlthoughMgCO3reactssimilarlywithhydrochloricacidandCaCO3withhydrochloricacid,becauseMgCO3hasfewersources,itisnotasgoodasCaCO3Cheapandeasytoget.(Magnesiumsaltisnotascheapascalciumsalt)
⑧Nitricacidcannotbeusedinsteadofhydrochloricacid.Thereason:nitricacidiseasytodecomposewhenexposedtolight().Ifnitricacidisusedinsteadofhydrochloricacid,theobtainedCOTherewillbeasmallamountofNO2andO2in2.Inaddition,nitricacidismoreexpensivethanhydrochloricacid,sonitricacidisusuallynotusedinsteadofhydrochloricacid.(Nitricacidiseasytodecomposewhenexposedtolight)
⑨Becausecarbondioxidecanextinguishthefire,aburningmatchcanbeplacedatthemouthofthegascylinderforinspection.Iftheflamegoesout,itprovesthatthegascylinderhasbeenfilledwithcarbondioxide.(Identifythatmatchesarenotcombustible)
Heattodecomposesodiumbicarbonatetoprepare
Afterthesodiumbicarbonateisfullydried,itisputintoahardglasstube,andthemouthofthetubeisfilledwithglasswoolandthensealed,andvacuumisdrawnwithanairpump.Then,heatingdecomposessodiumbicarbonate.Thefirstcarbondioxidecanbereleased.Thegasproducedbythedecompositionneedstobeintroducedintoanice-cooledpipetocondensethewatervaporinthegas,andthenthegasisintroducedintoU-shapedtubescontainingcalciumchlorideandphosphoruspentoxidetodrythem.At100°C,thedecompositionpressureofsodiumbicarbonateis97.458kPa,andat120°Citis166.652kPa.
Otherpreparationmethods
Whenbakingsoda(themaincomponentissodiumbicarbonate)andwhitevinegararemixedtogether,ametathesisreactionoccursandcarbondioxidegasisreleased.Thecorrespondingchemicalreactionequationis:.
Mainapplications
High-puritycarbondioxideismainlyusedintheelectronicsindustry,medicalresearchandclinicaldiagnosis,carbondioxidelasers,calibrationgasfortestinginstrumentsandthepreparationofotherspecialmixedgas.Itisusedasaregulatorinthepolymerizationreaction.
Solidcarbondioxideiswidelyusedinrefrigerateddairyproducts,meat,frozenfoodandotherfoodsthatareperishableintransit.Itisusedasarefrigerantinmanyindustrialprocesses,suchascrushingheat-sensitivematerials,rubberpolishing,andmetalColdprocessing,shrinkassemblyofmechanicalparts,vacuumcoldtraps,etc.
Gaseouscarbondioxideisusedforcarbonizationofsoftdrinks,pHcontrolinwatertreatmentprocesses,chemicalprocessing,foodpreservation,inertprotectioninchemistryandfoodprocessing,weldinggas,plantgrowthstimulant,andhardeningincastingMoldsandcoresandusedinpneumaticdevices,andalsousedasadiluentforsterilizinggas(thatis,usingamixtureofethyleneoxideandcarbondioxideasasterilization,insecticide,andfumigant.Itiswidelyusedinmedicalappliances,packagingmaterials,andclothing,Fur,bedding,etc.,sterilizationofbonemeal,fumigationofwarehouses,factories,culturalrelics,books).
Liquidcarbondioxideisusedasarefrigerant,low-temperaturetestsofaircraft,missilesandelectroniccomponents,toimproveoilwellrecovery,rubberpolishingandchemicalreactioncontrol,andcanalsobeusedasafireextinguishingagent.
Supercriticalcarbondioxidecanbeusedasasolventtodissolvenon-polar,non-ionic,andlow-molecular-weightcompounds,soitiswidelyusedinhomogeneousreactions.
Calculationofchemicaldata
Calculationreferencevalueofhydrophobicparameter(XlogP) | 0.9 |
Numberofhydrogenbondacceptors | 2 |
Topologicalmolecularpolarsurfacearea | 34.1 |
Numberofheavyatoms | 3 |
Complexity | 18.3 |
Numberofcovalentbondunits | 1 |
(Tablereference:)
Safetymeasures
Naturalenvironmentaspects
Environmentalhazards
Naturalgreenhouseeffect:greenhousegasessuchascarbondioxideintheatmospherecanstronglyabsorblong-waveradiationfromtheground.Long-waveradiationwithalongerwavelengthisradiatedtotheground,whichplaysaroleininsulatingtheground.
Enhancedgreenhouseeffect:SincetheIndustrialRevolution,humanactivitieshaveemittedalargeamountofgreenhousegasessuchascarbondioxide,whichhascausedtheconcentrationofgreenhousegasesintheatmospheretorisesharply,resultinginanincreasinggreenhouseeffect.Accordingtostatistics,beforeindustrialization,theglobalaverageannualatmosphericcarbondioxideconcentrationwas278ppm(1ppmisonepartpermillion).In2012,theglobalaverageannualatmosphericcarbondioxideconcentrationwas393.1ppm.ByApril2014,themonthlyaveragecarbondioxideconcentrationintheatmosphereofthenorthernhemisphereItexceeded400ppmforthefirsttime.
Globalwarming:Theincreasinggreenhouseeffectoftheatmospherehasledtoglobalwarming,resultinginaseriesofglobalclimateproblemsthatareunpredictablebysciencetoday.AccordingtotheInternationalEconomicsofClimateChangeReport,ifhumanbeingscontinuetomaintaintheircurrentlifestyles,by2100,thereisa50%chancethattheglobalaveragetemperaturewillriseby4°C.Iftheglobaltemperaturerisesby4℃,theglaciersinthenorthandsouthpolesoftheearthwillmelt,andthesealevelwillriseasaresult.Morethan40islandcountriesandthemostpopulouscoastalcitiesintheworldwillbeindangerofbeingsubmerged,withtensofmillionsofpeopleworldwide.Hislifewillfaceacrisis,andevenaglobalecologicalbalancedisorderwilleventuallyleadtolarge-scalemigrationandconflictsaroundtheworld.
Countermeasures
Low-carbonlife:MinimizetheconsumptionindailylifeEnergyneeds,therebyreducingcarbondioxideemissions,reducingairpollution,andslowingdownecologicaldegradation.
CCStechnology:carbondioxidecaptureandstorage(CarbonDioxideCaptureandStorage,abbreviation:CCS)technology,isoneofthemostimportanttechnologiestodealwithglobalclimatechangeintheshortterm,referringtotheuseofcarboncapturetechnology,Separatethecarbondioxideproducedbyindustryandrelatedenergyindustries,andthentransportandsealittotheseabedorunderground,etc.,whichisisolatedfromtheatmosphere,throughstoragemeans.
Internationallaw:AttheUnitedNationsConferenceonEnvironmentandDevelopmentheldinBrazilinJune1992,153countriessignedtheUnitedNationsFrameworkConventiononClimateChange.ThisconventionhasbeeneffectivesinceMarch1994.Thereare176contractingparties(asofFebruary2015);InDecember1997,ameetingattendedbyparticipatingcountriesofthe"JointFrameworkConventiononClimateChange"washeldinKyoto,Japan.Themeetingformulatedthe"KyotoProtocol"asthe"JointFrameworkConventiononClimateChange".AsupplementaryclausetotheFrameworkConventiononChange.ThistreatyhasbeeneffectivesinceFebruary16,2005,andhas183contractingparties(asofFebruary2009);November30-December11,2015,heldinParisAtthe21stConferenceofthePartiestothe"JointFrameworkConventiononClimateChange"andthe11thConferenceofthePartiestothe"KyotoProtocol",representativesfrom195countriesunanimouslyadoptedthe"ParisAgreementoftheUnitedNationsFrameworkConventiononClimateChange"("ParisAgreement").
Intermsofhumanhealth
Researchshowsthatwhentheconcentrationofcarbondioxideintheairislessthan2%,thereisnoobviousharmtohumans.Iftheconcentrationexceedsthisconcentration,itcancausedamagetothehumanrespiratoryorgans.Undercircumstances,carbondioxideisnotatoxicsubstance,butwhentheconcentrationofcarbondioxideintheairexceedsacertainlimit,thebodywillbepoisoned,andhighconcentrationsofcarbondioxidewillsuffocatepeople.Animalexperimentshaveprovedthat:intheairwithnormaloxygencontent(20%),thehighertheconcentrationofcarbondioxide,thehigherthemortalityofanimals.Atthesametime,purecarbondioxidecausesanimaldeathsanddeathscausedbyloweroxygenaremorerapid.Inaddition,somepeoplebelievethatinthecaseoflowoxygen,carbondioxideataconcentrationof8%to10%cancausedeathsofhumansandanimalsinashortperiodoftime.
Principleofpoisoning
High-concentrationcarbondioxideitselfhasstimulatingandanestheticeffectsandcancausehypoxiaandasphyxiationinthebody.
Symptomsofpoisoning
Mild:Generaldiscomfortsuchasdizziness,headache,muscleweakness,andbodyaches.
Moderate:dizzinessmayfalltotheground;chesttightness,unbearablepaininthenasalcavityandthroat,shortnessofbreath,pressureandsuffocationinthechest;severeheadache,tinnitus,muscleweakness,redskin,Bloodpressurerises,pulseisfastandstrong.
Severe:Suddenlydizzyandunabletosupport,falltotheground,holdbreath,dyspnea,palpitations,unconsciousness,coma,bruisingskin,lipsandnails,dropinbloodpressure,weakpulsetoreach,anddilatedpupils.Thelightreflexdisappears,thewholebodyissoft,theglottisisenlarged,andthebreathingandheartbeatstoponeafteranotheruntildeath.Somesymptomssuchaslethargyandmemorylossmayremainaftertheacuteperiod.
Firstaidmeasures
①Quicklygetthepoisonedpersonoutofthehigh-concentrationcarbondioxideenvironment,gotothefreshair,loosenthepoisonedperson’scollar,artificialassistanceBreatheinordertobreatheinoxygenassoonaspossible,andtreatwithhyperbaricoxygenifnecessary.Rescuersshouldweareffectiverespiratoryprotectiveequipment.
②Injectrespiratorystimulants,andantibioticsforsecondaryinfections;intravenousinfusionofsodiumbicarbonateorsodiumlactateforreducedcarbondioxidebindingcapacity;largerdosesofsedativesforlimbspasm;long-termhighfeverandconvulsionsSedativedrugscanbeused;othersymptomatictreatmentssuchaspulmonaryedemaandcerebraledema.
Precautions
Beforeenteringaworkareawithahigherconcentrationofcarbondioxide,checkwhethertheconcentrationofcarbondioxideintheairexceeds2%.Ifitexceeds,youneedtoTakeeffectivesafetymeasures,suchas:①Ventilationanddetoxification,replacingtheairintheworkplace,sothattheconcentrationofcarbondioxideintheairdoesnotexceed2%;②Wearingventilationmasks,self-primingductgasmasks,oxygenbreathingapparatusandothercommonlyusedanti-virusmask.
Storageprecautions
Carbondioxideissuitableforstorageinacool,ventilatednon-combustiblegaswarehouse,suitableforshipmentinliquidorsolidform.Payattentiontothefollowingpointswhenstoringandtransportingcarbondioxide:①Keepawayfromfireandheatsources,andthestoragetemperatureshouldnotexceed30℃;②Storeseparatelyfromeasily(combustible)materialsandavoidmixedstorage;③Thestorageareashouldbeequippedwithleakageemergencytreatmentequipment.
Relevantlawsandregulations
InChina,carbondioxideisreleasedonApril12,2007andimplementedonNovember1,2007.Part1:OccupationalExposureLimitsforHazardousFactorsintheWorkplace:Forthe90thsubstancein"ChemicalHarmfulFactors"(GBZ2.1-2007),intermsofhygienerequirements,thepermissibleconcentration-timeweightedaverage(PC-TWA)intheworkplaceis9000mg/m3,Permissibleconcentration-ShortTermExposureLimit(PC-STEL)is18000mg/m3.Inaddition,thenationalregulationcloselyrelatedtocarbondioxideisthenationalstandard"Methodforthedeterminationofcarbondioxideintheairinpublicplaces"(GB/T18204.24-2000),whichstipulatesthemethodformeasuringtheconcentrationofcarbondioxideintheairinpublicplaces.ThisstandardhasbeenapprovedinSeptember2014.Replacedby"PublicPlaceHygieneInspectionMethodsPart2:ChemicalPollutants"(GB/T18204.2-2014)issuedonDecember3,2014andimplementedonDecember1,2014.Forthedetectionofcarbondioxide,thestandarddetectionmethodsrecommendedby"PublicPlaceSanitationInspectionMethodsPart2:ChemicalPollutants"include3detectionmethods,namely,non-spectralinfraredgasanalysis(theminimumdetectionconcentrationis0.01%),andgaschromatographyMethod(thelowestdetectableconcentrationis0.014%),volumetrictitrationmethod(thelowestdetectableconcentrationis0.001%).
IntheUnitedStates,theAmericanConferenceOFGovernmentalIndustrialHygienists(ACGIH)thresholdconcentration,theOccupationalSafetyandHealthAdministration(OccupationalSafetyandHealthAdministration,OSHA)allowableconcentrationvaluesandTherecommendedconcentrationvalueoftheNationalInstituteforOccupationalSafetyandHealth(NIOSH)is5000ppm(5000×10-6).
