Definition
Microsoft Windows2000, XP, Win7 and IE, Office also supports WebDAV, which greatly enhances the value of web applications, and performance. For users who need a lot of publishing content, application WebDAV can reduce the dependence on the CMS system, and can be more freely created. Upload, download is easy.
Web Distributed Creative and Version Management (WebDAV) extends the HTTP / 1.1 protocol, allows clients to publish, lock and manage resources on the web, and is integrated with IIS.
WebDAV allows the client to perform the following operations
processing resources on the WebDAV publishing directory on the server. With this feature, its advantages, for example:
1. Users with correct permissions can copy and move files in the WebDAV directory.
2. Modify the properties associated with certain resources. For example, the user can write and retrieve the attribute information of the file.
3. Lock and unlock the resources so that multiple users can read a file at the same time. But each time there can be only one to modify the file.
4. Search the content and properties of the file in the webdav directory.
Sets the WebDAV publishing directory on the server as simple as the virtual directory of setting the virtual directory via the Internet Information Service Management unit. After setting the publishing directory, users with appropriate permissions can publish documents to the server and process files in the directory. You must first install Windows XP Professional before setting up a WebDAV directory.
WebDAV client
can be used by any of the Microsoft products described in the following list or clients through other arbitrary support industry standard WebDAV protocols. Access the WebDAV publishing directory.
· Windows XP is connected to the WebDAV server via "Add Online Neighbor Wizard" and displays the content in the webdav directory, as it is an integral part of the same file system on the local computer. After the connection is complete, you can drag and drop file, retrieve, and modify file properties, and perform many other file system tasks.
· Internet Explorer 5.0 Connects to the WebDAV Directory allows you to perform file system tasks that can be performed by Windows XP.
· Office 2000 creates, publishes, edits, publishes, and edits them directly into the WebDAV directory.
· In addition, some third-party Windows programs can be connected to the WebDAV server, showing the WebDAV directory content, rename, delete, and upload and download their files.
• Some Android applications can be implemented in the Android client to access WebDAV services.
Search for
in WebDAV, you can quickly search for the contents and properties of the files in this directory. For example, you can search all files containing
Table or all files written by Fred.
Integrated Security
Since WebDAV has been integrated with Windows XP and IIS, it has the security features provided by both. These include the IIS permissions specified in the Internet Information Services management unit and the free selection access control list (DACL) in the NTFS file system. For information on IIS security, see Security .
Due to the client with appropriate permissions, the WebDAV directory can be written, so it is important to control which client access directories is always important. To help you control access, IIS has built-in support for the Kerberos 5 authentication protocol, enhancing the functionality of integrating Windows authentication. Select Integrated Windows Authentication, you can ensure that only accessible clients can access the WebDAV directory on the intranet and write it on it. For more information about how the Kerberos 5 authentication protocol is integrated with IIS Integration Windows authentication collaboration, see Integrating Windows Authentication. For overall information about the Working principle of the Kerberos protocol, see "Kerberos V5 Authentication" in the Windows XP document.
Additionally, IIS also supports a summary authentication and advanced abstract authentication. Summary Authentication and Advanced Summary Authentication For the Windows Domain Server, providing more stringent security measures for passwords and through Internet Transport information. For information on abstract authentication, see Summary Authentication and Configuration Summary Authentication. For information on advanced abstract authentication, see Advanced Summary Authentication and Configuring Advanced Summary Authentication.
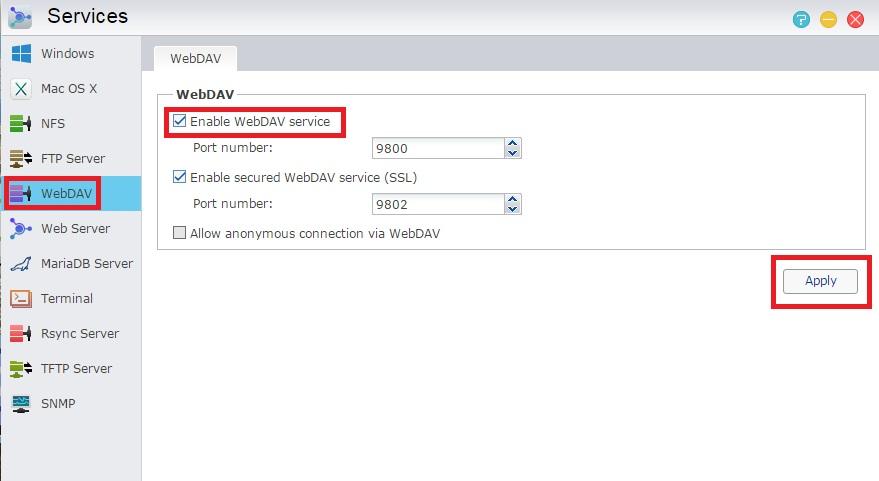
Advantages
Since the Web has become the foundation of the Internet, HTTP 1.1 (hypertext transfer protocol) is confirmed to be a very flexible general protocol for transmitting data. However, HTTP has some obvious disadvantages to limit it as a comprehensive Internet communication protocol: it is ideal for viewing static documents, but cannot provide sufficiently complex (in order to provide a rich creation function to the client) The method of processing documents.
For example, when two authors change a document while making a document, there is a "update loss" problem. Only by the last author is completed and the modified document is re-loaded to the server, the other author's changes will be lost.
The goal of the IETF WebDAV Working Group is to design an agreement that provides features that are required for any distributed creation tools in a standard forum. Current WebDAV Specification (IETF RFC 2518) Solve three major issues of collaborative creative tools:
· Remote protection . HTTP 1.1 cannot ensure that the client protects resources and can be changed while editing them at the same time. With WebDAV, you can lock resources in a variety of ways to let other clients know that you are interested in the resources discussed, or prevent other clients from accessing the resource.
· Resource Management . HTTP can only access a single resource directly. WEBDAV provides a method of organizing data more efficiently. WebDAV introduces a collection of resources (similar to the file system folder) concept. Resource management through WebDAV includes the following functions: Creating, Moving, Copying, and Delete a collection, as well as resources or files in the collection.
· Document property . Different types of data have unique properties, which helps to describe data. For example, in an email, these properties may be the time of the sender's name and the time of receiving the mail. In collaboration documents, these properties may be the name of the original author of the document and the name of the last editor. Because people's document types are different, the list of possible attribute types can also become unlimited. XML is an expandable communication tool required for WebDAV.
Request format
HTTP 1.1 (see IETF RFC 2068) Provides a group of methods that can be communicated with the server to the server, and specify a response (returning from the server) The format. WebDAV fully uses all methods in this specification, expand some of these methods, and introduces other methods that provide the description. The methods used in WebDAV include:
1.Options, Head and Trace.
is mainly used by the application to discover and track server support and network behavior.
2.get.
retrieves documents.
3.PUT and POST.
Submit a document to the server.
4.delete.
destroy resource or collection.
5. mkcol.
Create a collection.
6.Propfind and Proppatch.
Retrieves and sets the properties for resources and collections.
7.copy and move.
Manages the collection and resources in the namespace context.
8. LOCK and UNLOCK.
rewrite protection.
The general structure of the WebDAV request follows HTTP format.
and consists of the following three components:
1. Method. The method declares that the method executed by the client (the method described above).
2. Header. Describe instructions on how to complete this task.
3. Subject (optional). Define data used in this instruction or other instruction to describe how to complete this method.
In the main component, XML becomes a key element in the entire WebDAV structure.
