Historyofinvention
Netteddatabaseandhierarchicaldatabasehavesolvedtheproblemofdataconcentrationandsharing,butthereisstillagreatlackofdataindependenceandabstractionlevel.Whenusersaccessthesetwodatabases,theystillneedtoclarifythedatastoragestructureandpointouttheaccesspath.Buttherelationaldatabasethatappearedlatersolvedtheseproblemsbetter.Relationaldatabasetheoryappearedinthelate1960sandearly1970s.Therelationaldatamodelprovidesthecharacteristicsandfunctionalrequirementsofrelationaloperations,butdoesnotgivespecificgrammaticalrequirementsforthelanguageoftheDBMS.Theoperationoftherelationaldatabaseishighlynon-procedural,usersdonotneedtopointoutaspecialaccesspath,andtheselectionofthepathisdonebytheoptimizationmechanismoftheDBMS.
In1970,IBMresearcherDr.EFCoddpublished"RelationalModelofLargeSharedDataBanks"andproposedtheconceptofrelationalmodel,expoundingtheparadigmtheoryand12standardsformeasuringrelationalsystems,suchasthedefinitionCertainrelationalalgebraoperationsstudiedthefunctionalcorrelationofdataanddefinedthethirdparadigmofrelations,thuspioneeringthestudyofdatabaserelationalmethodsanddatanormalizationtheory.Forthis,hewontheTuringAwardin1981.
Later,Coddpublishedmanymorearticles,layingthefoundationofrelationaldatabase.Therelationalmodelhasastrictmathematicalfoundation,arelativelyhighlevelofabstraction,andissimpleandclear,easytounderstandanduse.Butatthattime,somepeoplethoughtthattherelationalmodelwasanidealizeddatamodel,anditwasunrealistictoimplementaDBMS.Theywereespeciallyworriedthattheperformanceofrelationaldatabaseswasunacceptable.Somepeopleevenregardeditasaseriousthreattothenormalizationworkofmeshdatabasesthatwasinprogressatthattime..Inordertopromoteunderstandingoftheproblem,ACMtooktheleadinorganizingaseminarin1974,duringwhichadebatebetweenthetwofactionsforandagainstrelationaldatabasesledbyCoddandBachmanwaslaunched.Thisfamousdebatepromotedthedevelopmentofrelationaldatabases,whicheventuallybecamethemainstreamofmoderndatabaseproducts.
Sincethen,manypeoplehaveturnedtheirresearchdirectionstorelationalmethods,andrelationaldatabasesystemshaveappearedoneafteranother.
Definition
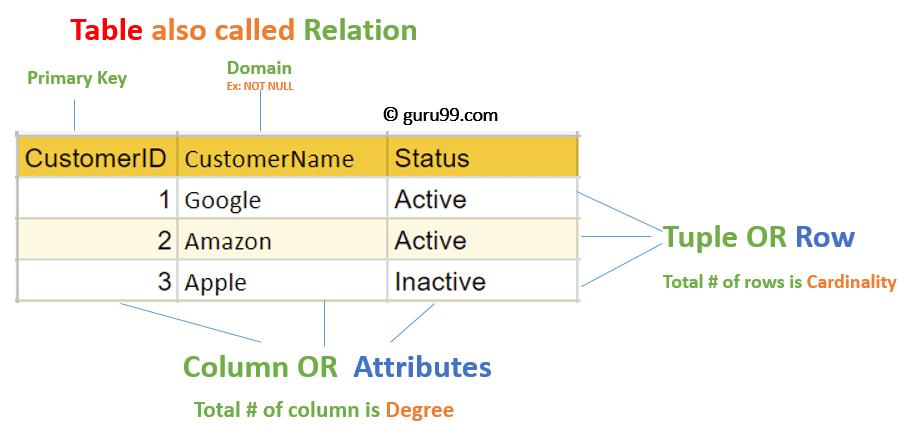
Therelationaldatamodelisdevelopedbasedontherelationalconceptinsettheory.Boththeentitiesandtheconnectionsbetweenentitiesintherelationalmodelarerepresentedbyasinglestructuretype-relationship.Therelationshipintheactualrelationaldatabaseisalsocalledatable.Arelationaldatabaseiscomposedofseveraltables.
Relationalmodelreferstoadatamodelthatusesatwo-dimensionaltabletorepresententitiesandtheirconnections.
Basicterms
Thereare13basicconceptsandbasictermsoftherelationalmodel.Theyare:
(1)Relation:arelationCorrespondstoatwo-dimensionaltable,andthetwo-dimensionaltableisthenameoftherelationship.
(2)Tuple:Arowinatwo-dimensionaltableiscalledatuple.
(3)Attribute:Thecolumnsinthetwo-dimensionaltablearecalledattributes.Thenumberofattributesiscalledthedegreeordegreeoftherelationship.Thevalueofthecolumniscalledtheattributevalue;
(4)(Value)Domain:Thevaluerangeoftheattributevalueisthevaluedomain.
(5)Component:theattributevalueofthecolumncorrespondingtoeachrow,thatis,anattributevalueinthetuple.
(6)Relationshipmode:Therowdefinitioninthetwo-dimensionaltable,thatis,thedescriptionoftherelationshipiscalledtherelationshipmode.Generallyexpressedas(attribute1,attribute2,...,attributen),suchastheteacher'srelationshipmodelcanbeexpressedasateacher(teachernumber,name,gender,age,title,department).
(7)Key(code):Ifthereisanattributeorattributesetthatuniquelyidentifiesanentityinarelationship,itiscalledthekeyoftheentity.Atuple,thecombinationofvaluesontheattributearealldifferent.
(8)Candidatekey(candidatecode):Ifthevalueofanattributeintherelationshipcanuniquelyidentifyatuple,ifnoattributecanberemovedfromakeyintherelationship,otherwiseitisnotThekeyofthisrelationshipiscalledthespecifiedcandidatekeyasthecandidatekeyorcandidatecodeoftherelationship.
Forexample,the"studentnumber"or"librarycardnumber"inthefollowingstudenttablecanuniquelyidentifyatuple,andthe"studentnumber"and"librarycardnumber"canbothuniquelyidentifyatuple.Then"studentnumber"and"librarycardnumber"canbeusedascandidatekeysforstudentrelations.
StudentID | Name | Gender | p>Age | Librarycardnumber | Department |
S3001 | ZhangMing | Male | 22 | B20050101 | Foreignlanguage |
S3002 | LiJing | Female | 21 | B20050102 | Foreignlanguage |
S4001 | ZhaoLi | Female | 21 | B20050301 | Manage |
Inthecourseselectiontable,onlytheattributegroups"studentnumber"and"coursenumber"canuniquelyidentifyatuple,andthecandidatekeyis(studentnumber,coursenumber).
StudentID | CourseID |
S3001 | C1 |
S3001 | C2 |
S3002 | C1 |
S4001 | C3 |
(8)Primarykey(primarycode):Specifyatupletouniquelyidentifytherelationshipamongthecandidatekeysofarelationship,thenthespecifiedcandidatekeyiscalledtheprimarykey,orsimplytheprimarykey,keyWord,maincode.Eachrelationshiphasandonlyoneprimarykey,usuallyasmallercombinationofattributesisusedastheprimarykey.Forexample,inthestudenttable,if"studentID"isselectedasthebasisfordataoperation,the"studentID"isthemainkey.Inthecourseselectiontable,theprimarykeyis(studentnumber,coursenumber).
(9)Primaryattributesandnon-primaryattributes:Theattributesincludedinanycandidatekeyintherelationshiparecalledprimaryattributes,andtheattributesnotincludedinanycandidatekeyarenon-primaryattributes.
(10)Fullkeyorfullcode:acollectionofallattributesinarelationalmodel.
(11)Foreignkeyorforeigncode:Althoughanattributeinarelationshipisnottheprimarykeyofthisrelationship,oronlytheprimarykey,butitistheprimarykeyofanotherrelationship,itiscalledforeignKeyorforeigncode.
(12)Superkeyorsupercode:Ifanattributeisremovedfromakeyofarelationship,itisstillthekeyoftherelationship,thensuchakeyiscalledthesuperkeyorsupercodeoftherelationship.
(13)Referencerelationshipandreferencedrelationship:refertotworelationshipsthatareconnectedbyforeignkeysandcanbetransformedintoeachother.
Two-dimensionaltable
Relationalmodel,fieldsarecalledattributes,fieldvaluesarecalledattributevalues,andrecordtypesarecalledrelationalmodels.ThenameoftherelationalschemaisR.Arecordiscalledatuple,andacollectionoftuplesiscalledarelationshiporinstance.Generally,uppercaselettersA,B,C,...areusedtoindicateasingleattribute,andlowercaselettersareusedtoindicateattributevalues.Thenumberofattributesintherelationshipiscalled"elementnumber",andthenumberoftuplesiscalled"cardinality".Therelationshipelementoftheexampleis5,andthebaseis2.Sometimesitisalsocalledarelationshipasatable,withtuplesasrowsandattributesascolumns.
Key
Key,alsoknownascode,consistsofoneorseveralattributes,dividedintothefollowingtypes:
a.Superkey:IfinrelationIfanattributeisremovedfromakeyof,itisstillthekeyofthisrelationship,andsuchakeybecomesasuperkey.
b.Candidatekeys:Superkeyswithoutextraattributesarecalledcandidatekeys.Thatis,ifyouwanttodeletetheattributeinthecandidatekey,itisnotasuperkey.
c.Primarykey:Acandidatekeyselectedbytheuserasatupleidentifieriscalledtheprimarykey.Ingeneral,thekeyreferstotheprimarykey.
Definitionandnatureofrelationship
RelationshipisacollectionoftupleswithelementnumberK(K>=1).
Relationshipisastandardizedform,andithasthefollowinglimitations:
a.Eachattributevalueintherelationshipisnotdecomposable.
b.Thesametuplesarenotallowedintherelationship.
c.Theorderoftuplesisnotconsideredintherelationship.
d.Theattributesinthetuplearealsounordered.
Relationalmode,relationalsub-mode,andstoragemode
Relationalmodel,theconceptualmodeisacollectionofrelationalmodes.Amodeisacollectionofrelationalsub-modes,andaninnermodeisacollectionofstoragemodes.
1.Relationalmode
Relationalmodeisactuallytherecordtype,including:modename,attributename,valuedomainname,andtheprimarykeyofthemode.Hedoesnotinvolvethedescriptionofphysicalstorage,onlythedescriptionofdatacharacteristics.
2.Relationshipsub-mode
Thesub-modeisthedescriptionofthepartofthedatausedbytheuser.Inadditiontopointingouttheuser'sdata,thecorrespondencebetweenthemodeandthesub-modeshouldalsobepointedout.
3.Storagemode
Thebasicorganizationofrelationalstorageisfiles,andtuplesarerecordsinfiles.Sincetherelationalmodelhaskeys,storingarelationcanberealizedbyhashingorindexing.
Threetypesofintegrityrulesoftherelationshipmodel
1.Entityintegrityrules
ThisrulerequirestuplesintherelationshipTherecanbenonullvaluesontheattributesthatmakeuptheprimarykey.Ifthereisanullvalue,thentheprimarykeyvaluewillnotbeabletouniquelyidentifythetuple.
2.Referentialintegrityrules
IftheattributesetKistheprimarykeyoftherelationalpatternR1,andKisalsotheforeignkeyoftherelationalpatternR2,thenintherelationshipofR2,thevalueofKistakenThereareonlytwopossibilitiesforthevalue,eithernullvalueorequaltoaprimarykeyvalueintheR1relationship.
Attentionshouldbepaidwhenusing:
a.Theforeignkeyandthecorrespondingprimarykeycanhavedifferentnames,aslongastheyaredefinedinthesamevaluerange.
b.R1andR2canalsobethesamerelationalmodel,whichrepresentstheconnectionbetweenattributes.
c.Whethertheforeignkeyvalueisallowedtobeemptyornotdependsonthespecificproblem.
3.User-definedintegrityrules
Thisisaconstraintforspecificdataanddependsontheapplicationenvironment.
Formaldefinitionofrelationalmodel
One,threecomponents:datastructure,dataoperationandintegrityrules.
1.Thebasicdatastructureoftherelationalmodelistherelation.
2.Relationaloperationsaredividedintorelationalalgebraandrelationalcalculus.
3.ThreetypesofintegrityrulesofRelationalModel.
Second,relationalalgebra
Dataoperationsinrelationaldatabasesaredividedintotwotypes:queryandupdate.Querystatementsareusedforvariousretrievaloperations,andupdateoperationsareusedforinsert,delete,andmodifyoperations.
Relationalquerylanguagesaredividedintotwocategoriesaccordingtotheirtheoreticalbasis:
1.Relationalalgebralanguage:queryoperationsareDMLlanguagesbasedonsetoperations.
2.Relationalcalculationlanguage:queryoperationisbasedontheDMLlanguagepredicatecalculation.
Fivebasicoperationsofrelationalalgebra
Relationalalgebraisasetofadvancedoperationswithrelationastheoperationobject.Arelationshipisdefinedasacollectionoftuplesofthesamenumber.Theelementsinthesetaretuples,andtheoperationsinrelationalalgebracanbedividedintotwocategories:
Traditionalsetoperations:union,difference,intersection,andCartesianproduct.
Expandedrelationaloperations:projection,selection,connectionandnaturalconnection,division.
1.Union
TherearetworelationsRandSthathavethesamerelationmode.TheunionofRandSisasetoftuplesbelongingtoRandS,rememberItisR∪S.
Note:RandShavethesameelementnumber.
2.Difference
TherearetworelationsRandSthathavethesamerelationmode.ThedifferencebetweenRandSisasetoftuplesthatbelongtoRbutnotS,DenotedasR-S.
Note:RandShavethesameelementnumber.
3.Cartesianproduct
SupposetheelementsoftherelationsRandSarerands,respectively.DefinetheCartesianproductofRandStobeasetof(r+s)tuples.Thefirstrcomponents(attributevalues)ofeachtuplecomefromatupleofR,andthelastscomponentscomefromatupleofS.,DenotedasR×S.
IfRhasMtuplesandShasntuples,thenR×Shasm×ntuples.
4.Selection
Findingalltuplesthatmeetthegivenconditionsfromtherelationshipiscalledselection.Theconditionisgivenbyalogicalexpression,andthetupleisselectedifthevalueofthelogicalexpressionistrue.Thisisanoperationperformedfromtheperspectiveofrows,thatis,tuplesareextractedinthehorizontaldirection.Theresultoftheselectionoperationcanformanewrelationship,andtherelationshipmoderemainsunchanged,butthenumberoftuplesislessthanorequaltothenumberoftuplesintheoriginalrelationship,whichisasubsetoftheoriginalrelationship.
Recordedas:δF(R)≡{t?tbelongstoR∧F(t)=true}
5.Projection
SelectfromtherelationshipThenewrelationshipcomposedofseveralattributesiscalledprojection.Thisisthecalculationfromtheperspectiveofthecolumn.Afterprojectionoperation,anewrelationshipcanbeobtained.Thenumberofattributescontainedintherelationshipisoftenlessthanthatoftheoriginalrelationship,ortheattributesarearrangedinadifferentorder.Ifthenewrelationshipcontainsduplicatetuples,theduplicatetuplesmustbedeleted.
Recordedas:∏A(R)={t[A]?tbelongstoR}AistheattributecolumninR.
Forexample:∏3,1(R)
Fourcombinationoperationsofrelationalalgebra
1.Cross
RelationshipRandTheintersectionofSisasetoftuplesthatbelongtoRandS,denotedasR∩S.RandSrequirementsaredefinedonthesamerelationalmodel.
R∩S≡{t?tbelongstoR∧tbelongstoS},RandShavethesamearity.
2.Connections
Therearetwokindsofconnections:θconnectionandFconnection(θisanarithmeticcomparisonsymbol,Fisaformula).
⑴Thetajoin
ThetajoinistoselecttupleswhoseattributevaluessatisfyacertainθoperationfromtheCartesianproductoftherelationsRandS,denotedas:
R?×iθj?S,whereiandjaretheserialnumbersofthei-thandj-thattributesintherelationsRandS,respectively.
R?×iθj?S≡δiθ(r+j)(R×S)
Ifθistheequalsign"=",theconnectionoperationiscalled"equalValueconnection".
⑵Fjoin
TheFjoinoperationistoselecttupleswhoseattributevaluessatisfyacertainformulaFfromtheCartesianproductoftherelationsRandS,denotedas:
R?×F?S,whereFisaformulaoftheformF1∧F2∧...∧Fn,eachfisaformulaoftheformiθj,andiandjarethefirstintherelationsRandS,respectivelyTheserialnumberofthei-thattributeandthej-thattribute.
3.Naturalconnection
ThenaturalconnectionofthetworelationsRandSisrepresentedbyR?×?S.Thespecificcalculationprocessisasfollows:
①CalculateR×S
②LetthecommonattributesofRandSbeA1,...,Ak,andselectR×SthatsatisfiesR.A1=S.A1,...,R.Ak=S.Aktuples
③RemovethesecolumnsofS.A1,...,S.Ak.
Ifthereisnocommonattributeinthetworelations,thenthenaturalconnectionistransformedintoaCartesianproductoperation.
4.Division
GivenrelationsR(X,Y)andS(Y,Z),X,Y,Zareattributegroups.YinRandYinScanhavedifferentattributenames,buttheymustcomefromthesamedomainset.ThedivisionoperationofRandSresultsinanewrelationshipP(X),wherePistheprojectionofthetupleinRthatmeetsthefollowingconditionsontheattributeX:theimagesetYXofthecomponentvaluexofthetupleonXcontainsSonYAcollectionofprojections.
Relationalalgebraexpressionsandexamplesoftheirapplications
Inrelationalalgebraoperations,theformulathatiscompoundedbyfivebasicoperationsthroughafinitenumberoftimesiscalledRelationalalgebraicexpressions.Theresultofthisexpressionisstillarelationship.Canuserelationalalgebraicexpressionstoexpressvariousdataqueryoperations.
Samplequestion:Supposetherearethreerelationshipsintheteachinglibrary:
StudentrelationshipS(S#,SNAME,AGE,SEX)
LearningrelationshipSC(S#,C#,GRADE)
CurriculumRelationshipC(C#,CNAME,TEACHER)
Thefollowingusesrelationalalgebraexpressionstoexpresseachquerystatement
1.SearchandlearnThestudentIDandgradeofthestudentwhosecoursenumberisC2.
2.RetrievethestudentIDandnameofthestudentwhosestudycoursenumberisC2.
3.RetrievethestudentIDandnameoftheelectivecoursenamedMATHS.
4.RetrievethestudentIDofthestudentwhoseelectivecoursenumberisC2orC4.
5.RetrievethestudentIDofatleasttheelectivecoursenumberC2orC4.
6.SearchforthenamesofstudentswhodonotstudyC2withage.
7.Retrievethenamesofstudentsstudyingallcourses.
1.∏S#,GRADE(δC#='C2'(SC))
or∏1,3(δ2='C2'
Relationshipmode
Relationshipmodeisthedescriptionoftherelationship.
R(U,D,dom,F)
Risthenameoftherelationship,andUconstitutestherelationshipAttributenamecollection,thedomainfromwhichtheattributesintheDattributegroupUcomefrom,themappingcollectionfromthedomattributetothedomain,andthedatadependencycollectionbetweentheattributesF.Forexample:thetutorandthegraduatestudentcomefromthesamedomain-people,takedifferentattributesName,anddefinethemappingofattributestodomainsinthepattern,thatis,whichdomainstheycomefrom:
dom(SUPERVISOR-PERSON)=dom(POSTGRADUATE-PERSON)=PERSON
Relationshipmodecanusuallybeabbreviatedas:
R(U)orR(A1,A2,...,An)
Rrelationname,A1,A2,...,AnattributeName,note:Themappingofdomainnamesandattributestodomainsisoftendirectlydescribedasthetypeandlengthofattributes.
Relationaldatabasesystemsaredatabasesystemsthatsupportrelationalmodels.
Thecharacteristicsare:singleconcept,standardized,expressedintwo-dimensionaltables.
Introduction
TherelationalmodelwasproposedbyEFCoddin1970.
ItComparedwiththehierarchicalandmeshmodel,ithasthefollowingcharacteristics:
1.Simpledatastructure(two-dimensionaltable)
2.Solidtheoreticalfoundation.
a.Relationaloperationtheory
b.Relationalmodeldesigntheory
Thebasicassumptionoftherelationalmodelisthatalldataareexpressedasmathematicalrelations,thatistosaynasubsetoftheCartesianproductofaset.Thereasoningaboutthisdataiscarriedoutthroughbinary(thatis,noNULL)predicatelogic,whichmeansthatthereareonlytwopossibleevaluationsforeachproposition:Eithertrueorfalse.Dataismanipulatedbyamethodofrelationalcalculusandrelationalalgebra.Relationalmodelisadatamodelthatusesatwo-dimensionaltablestructuretoexpressentitytypesandconnectionsbetweenentities.
RelationalmodelAllowsthedesignertobuildamodelofinformationconsistencythroughthestandardizationofthedatabase.TheaccessplanandotherimplementationandoperationdetailsareprocessedbytheDBMSengineandshouldnotbereflectedinthelogicalmodel.ThisisthecommonpracticeofSQLDBMSOpposite,whereperformanceadjustmentsoftenrequirechangestothelogicalmodel.
Thebasicbuildingblocksofrelationshipsaredomainsordatatypes.Tuplesareorderedmultisetsofattributes,andattributesaredomainsandAnorderedpairofvalues.Arelationalvariable(relvar)isacollectionoforderedpairs(orderedpairs)offieldsandnames,whichactastheheaderoftherelation.Arelationshipisacollectionoftuples.Althoughtheserelationalconceptsaremathematicallydefined,theycanbelooselymappedtotraditionaldatabaseconcepts.Tablesarerecognizedvisualrepresentationsofrelationships;tuplesaresimilartotheconceptofrows.
Thebasicprincipleoftherelationalmodelistheprincipleofinformation:allinformationisexpressedasdatavaluesintherelation.Therefore,relationalvariablesarenotrelatedtoeachotheratdesigntime;instead,thedesignerusesthesamedomaininmultiplerelationalvariables.Ifoneattributedependsonanotherattribute,referentialintegrityisusedtoenforcethisdependency.
Advantages
(1)Singledatastructure
Intherelationalmodel,whetheritisentitiesortheconnectionsbetweenentities,theyareallexpressedbyrelations,andrelationsAllcorrespondtoatwo-dimensionaldatatable,thedatastructureissimpleandclear.
(2)Therelationshipisstandardizedandestablishedonastricttheoreticalbasis
Thebasicnormsthatconstitutetherelationshiprequirethateachattributeintherelationshipcannotbeseparated,andtherelationshipisestablishedonasolidbasis.Thetheoreticalbasisisbasedonstrictmathematicalconcepts.
(3)Simpleconceptandeasyoperation
Thebiggestadvantageoftherelationalmodelissimplicity,whichiseasyforuserstounderstandandmaster.Arelationshipisatwo-dimensionaltable,andusersonlyneedtousesimplequeries.Thelanguagecanoperatethedatabase.
Composition
Relationaldatastructure
Singledatastructure-relationship
Real-worldentitiesandvariousconnectionsbetweenentitiesAllarerepresentedbyrelations.Fromtheuser'spointofview,thelogicalstructureofthedataintherelationalmodelisatwo-dimensionaltable.
Collectionofrelationaloperations
Commonlyusedrelationaloperationsincludequeryoperationsandinsert,delete,andmodifyoperations.Amongthem,theexpressionabilityofqueryoperationisthemostimportant,including:selection,projection,connection,division,union,intersection,difference,etc.
Intheearlystage,therelationaloperationabilityinrelationalmodelsisusuallyexpressedbyalgebraicmethodsorlogicalmethods,whicharecalledrelationalalgebraandrelationalcalculus,respectively.Relationalalgebraisawayofexpressingqueryrequirementsbyalgebraicoperationsonrelations;relationalcalculusisawayofexpressingqueryrequirementsbypredicates.ThereisalsoalanguagebetweenrelationalalgebraandrelationalcalculuscalledStructuredQueryLanguage,orSQLforshort.
Dataintegrityoftherelationship
Includes:domainintegrity,entityintegrity,referentialintegrityanduser-definedintegrity.
Domainintegrity:referstothevaluerangeoftheattribute,suchasgendershouldbemaleorfemale.
TheEntityIntegrityrule:IftheattributeAistheprimaryattributeofthebasicrelationshipR,thentheattributeAcannottakeanullvalue.Forexample:Inthecoursetable(coursenumber,coursename,teacher,weeklyclasshours,remarks),the"coursenumber"attributeistheprimarykey,thenthe"coursenumber"cannottakethesamevalue,norcanittakeanullvalue.
Referentialintegrityrules:Iftheattribute(orattributegroup)FistheforeignkeyofthebasicrelationshipR,itcorrespondstotheprimarykeyKsofthebasicrelationshipS(therelationshipRandSarenotnecessarilydifferentrelationships),ThenthevalueofeachtupleintherelationshipRontheattributeFmustbe:
1.Ortakeanullvalue(eachattributevalueinFisempty);
2.OrequaltotheprimarykeyvalueofatupleinS.
Forexample:employee(employeenumber,name,gender,departmentnumber,boss,salary,commission)
department(departmentnumber,name,location)
Theemployeenumberistheprimarykeyofthe"employee"relationship,thedepartmentnumberistheforeignkey,andthedepartmentnumberinthe"department"relationshipistheprimarykey,thenthedepartmentnumberattributeofeachtupleintheemployeerelationshipcanonlytakethefollowingtwotypesofvalues:
Type1:Nullvalue,whichmeansthattheemployeehasnotbeenassignedadepartment;
Type2:Non-emptyvalue,butthevaluemustbethedepartmentnumberofatupleinthedepartmentrelationshipValuemeansthattheemployeecannotbeassignedtoanon-existentdepartment,thatis,theremustbeatupleinthereferencedrelationship"department",anditsprimarykeyvalueisequaltotheforeignkeyvalueofthereferencerelationship"employee".
Domainintegrity,entityintegrityandreferentialintegrityaretheintegrityconstraintsthatmustbemetintherelationalmodel.Aslongasitisarelationaldatabasesystem,itshouldsupportdomainintegrity,entityintegrityandreferentialintegrity.Inaddition,differentrelationaldatabasesystemsoftenrequiresomespecialconstraintsaccordingtotheirapplicationenvironments,anduser-definedintegrityisaconstraintoncertainspecificrelationaldatabases.Forexample:courseselectiontable(coursenumber,studentnumber,grade).Whendefiningtherelationshipselectiontable,wecandefinetheconstraintthattheattributeofgrademustbegreaterthanorequalto0.
