Definition
Inmachinelearning,randomforestisaclassifierthatcontainsmultipledecisiontrees,andtheoutputcategoriesareoutputbyindividualtreesDependingonthemodeofthecategory.LeoBreimanandAdeleCutlerdevelopedanalgorithmtodeducerandomforests.And"RandomForests"istheirtrademark.ThistermisderivedfromrandomdecisionforestsproposedbyTinKamHoofBellLabsin1995.ThismethodcombinesBreimans'"Bootstrapaggregating"ideaandHo's"randomsubspacemethod"tobuildasetofdecisiontrees.
Learningalgorithm
Buildeachtreeaccordingtothefollowingalgorithm:
UseNtorepresenttrainingThenumberofusecases(samples),Mrepresentsthenumberoffeatures.
Enterthenumberoffeaturesmtodeterminethedecisionresultofanodeonthedecisiontree;wheremshouldbemuchsmallerthanM.
FromNtrainingcases(samples)withreplacementsampling,takesamplesNtimestoformAtrainingset(iebootstrapsampling),anduseun-selectedusecases(samples)tomakepredictionstoevaluatetheerror.
Foreachnode,randomlyselectmfeatures,andthedecisionofeachnodeonthedecisiontreeisdeterminedbasedonthesefeatures.Accordingtothesemcharacteristics,calculatethebestsplitmethod.
Eachtreewillgrowcompletelywithoutpruning,whichmaybeusedafteranormaltree-likeclassifierisbuilt).
Advantages
Theadvantagesofrandomforestare:
1)Formanykindsofdata,itcangeneratehighaccuracyClassifier;
2)Itcanhandlealargenumberofinputvariables;
3)Itcanevaluatetheimportanceofvariableswhendeterminingthecategory;
4)Whenbuildingtheforest,itcanproduceanunbiasedestimateofthegeneralizederrorinternally;
5)Itcontainsagoodmethodtoestimatethemissingdata,andifthereisalargepartoftheIfthedataismissing,theaccuracycanstillbemaintained;
6)Itprovidesanexperimentalmethodtodetectvariableinteractions;
7)Forunbalancedclassificationdatasets,Itcanbalanceerrors;
8)Itcalculatestheclosenessineachcase,whichisveryusefulfordatamining,detectingoutliersandvisualizingdata;
9)Usetheabove.Itcanbeextendedtounlabeleddata,whichusuallyusesunsupervisedclustering.Itcanalsodetectdeviatorsandwatchdata;
10)Thelearningprocessisveryfast.
Relatedconcepts
1.Split:Inthetrainingprocessofthedecisiontree,thetrainingdatasetneedstobesplitintotwosub-datasetsagainandagain.Thisprocessiscalledsplitting.
2.Features:Inaclassificationproblem,thedatainputintotheclassifieriscalledafeature.Taketheabovestockpriceforecastingproblemasanexample.Thecharacteristicisthetradingvolumeandclosingpriceofthepreviousday.
3.Featurestobeselected:Intheprocessofconstructingthedecisiontree,itisnecessarytoselectfeaturesfromallthefeaturesinacertainorder.Thefeaturestobeselectedarethesetoffeaturesthathavenotbeenselectedbeforethestep.Forexample,ifallthefeaturesareABCDE,inthefirststep,thecandidatefeatureisABCDE,andinthefirststep,Cisselected,theninthesecondstep,thecandidatefeatureisABDE.
4.Splitfeature:Thedefinitionofthereceptionselectionfeature.Eachselectedfeatureisthesplitfeature.Forexample,intheaboveexample,thefirstsplitfeatureisC.Becausetheseselectedfeaturesdividethedatasetintodisjointparts,theyarecalledsplitfeatures.
Decisiontreeconstruction
Totalkaboutrandomforest,wemustfirsttalkaboutdecisiontrees.Decisiontreeisabasicclassifier,whichgenerallydividesfeaturesintotwocategories(decisiontreecanalsobeusedforregression,butthisarticlewillnotshowitforthetimebeing).Theconstructeddecisiontreehasatreestructure,whichcanbeconsideredasacollectionofif-thenrules.Themainadvantageisthatthemodelisreadableandtheclassificationspeedisfast.
Weusetheprocessofselectingquantitativetoolstovisualizetheconstructionofthedecisiontree.Supposewewanttochooseanexcellentquantitativetooltohelpusbetterstocks,howtochoose?
Thefirststep:seeifthedataprovidedbythetoolisverycomprehensive,don’tuseitifthedataisnotcomprehensive.
Step2:CheckiftheAPIprovidedbythetooliseasytouse.IftheAPIisnotgood,don'tuseit.
Step3:Checkwhetherthebacktestingprocessofthetoolisreliable,andthestrategiesthatarenotreliablebacktestingarenotused.
Step4:Checkwhetherthetoolsupportssimulatedtrading.Backtestingonlyallowsyoutojudgewhetherthestrategyisusefulinhistory.Atleastasimulateddiskisneededbeforetheformaloperation.
Inthisway,thequantitativetoolsonthemarketwillbelabeledby"whetherthedataiscomprehensive","whethertheAPIiseasytouse","whetherthebacktestisreliable",and"whethersimulatedtradingissupported"."Use"and"Donotuse".
Theaboveistheconstructionofadecisiontree,andthelogiccanberepresentedinFigure1:
InFigure1,the"data","API"and"backtest"inthegreencolorbox"Simulatedtrading"isafeatureinthisdecisiontree.Iftheorderofthefeaturesisdifferent,thedecisiontreeconstructedfromthesamedatasetmayalsobedifferent.Theorderoffeaturesis"data","API","backtest"and"simulatedtransaction".Ifweselectthefeaturesintheorderof"data","simulatedtrading","API"and"backtest",thenthedecisiontreeconstructediscompletelydifferent.
Itcanbeseenthatthemainjobofthedecisiontreeistoselectfeaturestodividethedataset,andfinallyputthedataontwodifferenttypesoflabels.Howtochoosethebestfeature?Alsousetheexampleofselectingquantizationtoolsabove:supposethereare100quantizationtoolsonthemarketasthetrainingdataset,andthesequantizationtoolshavebeenlabeled"available"and"unavailable".
Wefirsttriedtodividethedatasetintotwocategoriesby"IstheAPIeasytouse";wefoundthattheAPIsof90quantitativetoolsareeasytouse,andtheAPIsof10quantitativetoolsarenoteasytouse.Amongthe90quantitativetools,40arelabeledas"available"and50arelabeledas"unavailable".Then,theclassificationeffectofthe"APIiseasytouse"onthedataisnotEspeciallygood.Because,givenyouanewquantitativetool,evenifitsAPIiseasytouse,youstillcannotlabelitas"used"well.
Assumeagainthatthesame100quantitativetoolscanbedividedintotwocategoriesby"Doyousupportsimulatedtrading".Onecategoryhas40quantitativetooldata,andall40quantitativetoolssupportSimulatedtransactionswereeventuallylabeled"used".Anothercategoryhad60quantitativetools,noneofwhichsupportedsimulatedtransactions,andtheywereeventuallylabeled"notused".Ifanewquantitativetoolsupportssimulatedtrading,youcanjudgewhetherthequantitativetoolcanbeused.Webelievethattheclassificationofdataby"whetheritsupportssimulatedtrading"isveryeffective.
Inreal-worldapplications,datasetsoftenfailtoachievetheabove-mentionedclassificationeffectof"whethersimulatedtradingissupported".Soweusedifferentcriteriatomeasurethecontributionoffeatures.Threemainstreamcriteriaarelisted:ID3algorithm(proposedbyJ.RossQuinlanin1986)usesthefeaturewiththelargestinformationgain;C4.5algorithm(proposedbyJ.RossQuinlanin1993)usestheinformationgainratiotoselectfeatures;CARTalgorithm(Breimanetal.(proposedin1984)usetheGiniindexminimizationcriterionforfeatureselection.
Randomforestconstruction
Thedecisiontreeisequivalenttoamaster,classifyingnewdatathroughtheknowledgelearnedinthedataset.Butasthesayinggoes,oneZhugeLiangcan'tplaywiththreeheads.Randomforestisanalgorithmthathopestobuildmultipleheadsandhopesthatthefinalclassificationeffectcanexceedasinglemaster.
Howtobuildarandomforest?Therearetwoaspects:randomselectionofdata,andrandomselectionoffeaturestobeselected.
1.Randomselectionofdata:
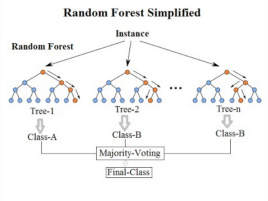
First,takeasamplewithreplacementfromtheoriginaldatasettoconstructasub-dataset.Thedatavolumeofthesub-datasetisthesameastheoriginaldata.Setthesame.Elementsindifferentsub-datasetscanberepeated,andelementsinthesamesub-datasetcanalsoberepeated.Second,usesub-datasetstoconstructsub-decisiontrees,putthisdataineachsub-decisiontree,andeachsub-decisiontreeoutputsaresult.Finally,ifthereisnewdatathatneedstobeclassifiedthroughtherandomforest,theoutputresultoftherandomforestcanbeobtainedbyvotingonthejudgmentresultsofthesub-decisiontree.AsshowninFigure3,assumingthatthereare3sub-decisiontreesintherandomforest,theclassificationresultof2sub-treesistypeA,andtheclassificationresultof1sub-treeistypeB,thentheclassificationresultoftherandomforestistypeA.
2.Randomselectionoffeaturestobeselected
Similartorandomselectionofdatasets,eachsplittingprocessofthesubtreeintherandomforestdoesnotuseallthefeaturestobeselected,Butrandomlyselectacertainfeaturefromallthefeaturestobeselected,andthenselecttheoptimalfeaturefromtherandomlyselectedfeatures.Inthisway,thedecisiontreesintherandomforestcanbedifferentfromeachother,andthediversityofthesystemisimproved,therebyimprovingtheclassificationperformance.
InFigure4,thebluesquaresrepresentallthefeaturesthatcanbeselected,thatis,thefeaturestobeselected.Theyellowsquareisasplitfeature.Ontheleftisthefeatureselectionprocessofadecisiontree.Splittingiscompletedbyselectingtheoptimalsplitfeaturefromthefeaturestobeselected(don'tforgettheID3algorithm,C4.5algorithm,CARTalgorithm,etc.mentionedabove).Ontherightisthefeatureselectionprocessofasubtreeinarandomforest.
