Úvod
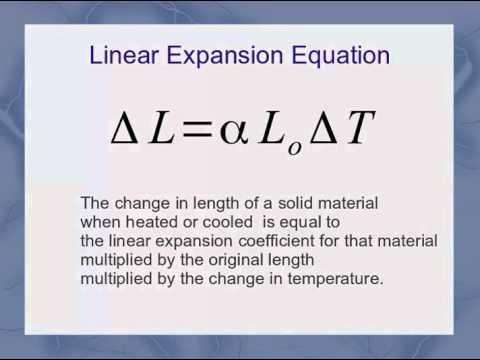
Také známý jako lineární expanzní koeficient. Když se teplota pevné látky zvýší o 1 °C, prodloužení na jednotku délky se nazývá "lineární expanzní koeficient". Jednotka 1/℃ nebo 1/K. Symbol je αl. Definice je (viz obrázek)
tedy
lt=l0(l+al△t).
Duetodifferentmaterials,thecoefficientoflinearexpansionisalsodifferent,anditsvalueisalsorelatedtotheactualtemperatureandthereferencetemperatureselectedwhendeterminingthelength1,butbecausethelinearexpansioncoefficientofsolidsdoesnotchangemuch,usuallyItcanbeignored,andaisregardedasaconstantindependentoftemperature.
Thecoefficientoflinearexpansionofmaterialsisavailableinthe"MachineDesignManual".
Variační zákon
Thelawoflinearexpansioncoefficientchangingwithtemperatureissimilartothatofheatcapacity.Theavalueisverysmallatverylowtemperature,anditincreasesquicklywiththeincreaseoftemperature,andtendstobeconstantabovetheDebyecharacteristictemperature.Theabsolutevalueofthelinearexpansioncoefficientiscloselyrelatedtothecrystalstructureandbondstrength.Materialswithhighbondstrengthhavealowcoefficientoflinearexpansion.Comparedwithmetalmaterials,refractorymaterialshavestrongbondsandsmalllinearexpansioncoefficients.Generally,theαvalueofoxideisintherangeof(8~15)×10K,theαvalueofbinarysilicatematerialisgenerally(5.2~10)×10K,theavalueofcarbideis(5~7)×10Kdiamond1×1010Kquartzglassisduetotherelaxationofitsstructure,thelinearexpansionofthetetrahedroninthestructureisaccommodatedbythevoidsinthestructure,andhasaverysmallavalue(0.5×1010Knon-equaxialcrystalsalongdifferentcrystalaxesTheavalueisdifferent,especiallyformaterialswithalayeredstructuresuchasgraphite.Graphitehasastronginterlayerbondingforce,withasmalllayer-wiseavalue(1×1010K),andaweakinterlayerbondingforce,withavalueof27×intheinterlayerdirection.10KForcrystalswithstrongnon-equaxiality,thevalueofninacertaindirectionmaybenegative.Refractorymaterialscomposedofanisotropicpolycrystalsandrefractorymaterialscomposedofmultiphasepolycrystalswithdifferentphaseavalues,Internalstresswillbegeneratedinthematerialduringthefiringandcoolingprocess.Whenthegrainboundaryisinahighstressstate,thestrengthofthematerialwilldecrease,andevenmicrocrackswilloccur.Theporosityalsohasaneffectonthethermalexpansioncharacteristicsoftherefractory.Whentheporesmaketheparticlesinthematerialinter-particlesWhenthebondbecomesweaker,theavaluebecomessmaller.Theclosedsmallporesinthecontinuoussolidphasehardlyaffecttheavalue.Thelinearexpansioncoefficientofmultiphasepolycrystallineandcompositematerialscanbecalculatedbasedonthephasecomposition.AllcalculationformulasAllarebasedonthepremisethatnomicro-cracksaregeneratedundertheactionofinternalstressbetweenthephases,soitisactuallyanapproximateestimation.Forrefractorymaterialswithmultiplemicro-cracks,thedeviationofthemeasuredvalueandthecalculatedvalueofacanbeusedasameasureofmicro-crack.Ameasureofthenumberofdefectsinthestructure.
Metoda měření
Thecommonlyusedmethodsformeasuringthelinearexpansioncoefficientofrefractorymaterialsaretheindirectmethodoftheejectorrodandthedirectreadingmethodofthetelescope.ThenewlasermethodThedeterminationofthecoefficientoflinearexpansionhasalsoreceivedmoreandmoreattention.
Typ ejektoru nepřímá metoda
Theejectormethodisaclassicmethod,whichusestheprincipleofmechanicalmeasurement,tedyoneendofthesampleisfixedOntheendofthesupporter,theotherendisincontactwiththeejectorrod,thesample,thesupporterandtheejectorrodareheatedatthesametime,andthethermalexpansiondifferencebetweenthesampleandthesepartsistransmittedbytheejectorrodandmeasured.Itcanbedividedintovarioustypesofinstrumentsaccordingtotheposition(verticalorhorizontal)andthemeasurementmethodofexpansion(directmeasurement,electronicoropticalmethod).Themostcommonapplicationistheinductivedilatometer.Itssensorisadifferentialtransformer,Alsocalleddifferentialtransformerthermaldilatometer.Duetothelongsizeoftheejectorrodandthesupporter,theheatingconditionsofthehigh-temperaturefurnacearedifficulttomakethetemperaturedistributionuniform,andtheexpansionbetweentheejectorrodandthesupporterisdifficulttooffseteachother,sothemeasuredvalueofexpansionNeedtobecorrected.
Metoda přímého čtení teleskopem
Thetelescopedirectreadingmethodusesbinocularstodirectlyobservethechangevalueofthesampleexpansionunderhightemperatureinthefurnace,andobtainthelinearexpansioncoefficientthroughcalculation.Themeasurementtemperaturecanbeashighas2000℃,andthemicrometerontheeyepiecedirectlymeasurestheelongationofthesample.Thesampleusedislong,andtheheatingfurnacemusthaveenoughconstanttemperaturezone.Thedisadvantageofthismethodisthatitisgenerallynoteasytorecordautomatically.NowithasbeendevelopedAutomaticrecordingsystemfortimedphotography.
Laserové měření
Thermalexpansionhasdevelopedinrecentyears.Itscansthesamplewithalaserbeamandcontinuouslymeasuresthechangeinlengthofthesampleduringtheheatingprocess.Itispopularbecauseofitshighmeasurementaccuracyandthefullyautomaticcontrol,recordingandmulti-functionsystemcomposedofcomputers.Whenchoosingathermalexpansionmeasurementmethod,themainconsiderationisthetestrange,thetypeandcharacteristicsofthematerialtobetested,themeasurementaccuracyandsensitivity,etc.
Životní aplikace
Thecoefficientoflinearexpansionisoneoftheimportantpropertiesthatshouldbeconsideredwhenusingrefractories.Thefurnaceisusuallybuiltatroomtemperature,andthefurnacebodyexpandswhenusedathightemperature.Inordertooffsetthestresscausedbythermalexpansion,expansionjointsneedtobereserved.Thecoefficientoflinearexpansionisakeyparameterforthestructuraldesigncalculationofthereservedexpansionjointsandtheoverallsizeofthemasonry.Itiscloselyrelatedtothethermalshockresistanceofthematerialandthedistributionandsizeoftheinternalthermalstressofthematerialduringthermalshock.Inthemanufactureofcompositematerialsandmultiphasematerials,theinfluenceofthematchinganddifferenceoftheirlinearexpansioncoefficientsonthestructureandperformancemustbeconsidered.Inaddition,bymeasuringthecurveofthelinearexpansioncoefficientofthematerialwiththetemperature,itispossibletostudythematerialmineralanalysis,phasetransition,andthehealingandpropagationofmicrocracks.
Ovlivňující faktory
1:Chemicalmineralcomposition.Thecoefficientofthermalexpansionisrelatedtothechemicalcomposition,crystallinestate,crystalstructure,andbondstrengthofthematerial.Substanceswiththesamecompositionanddifferentstructurehavedifferentexpansioncoefficients.Undernormalcircumstances,crystalswithatightstructurehavealargeexpansioncoefficient;whilesimilartoamorphousglass,theyoftenhaveasmallexpansioncoefficient.Materialswithhighbondstrengthgenerallyhavealowcoefficientofexpansion.
2:Phasechange.Whenamaterialundergoesaphasechange,itsthermalexpansioncoefficientalsochanges.Whenthepuremetalallotropetransforms,thelatticestructurerearrangementisaccompaniedbythemutationofthemetalspecificvolume,whichleadstothediscontinuouschangeofthelinearexpansioncoefficient.
3:Alloyingelementshaveaneffectonthethermalexpansionofthealloy.Theexpansioncoefficientofasingle-phaseuniformsolidsolutionalloycomposedofsimplemetalsandnon-ferromagneticmetalsisbetweentheexpansioncoefficientsoftheinternalcomponents.Theexpansioncoefficientofamultiphasealloydependsonthenatureandquantityoftheconstituentphases,andcanberoughlycalculatedaccordingtothevolumepercentageoccupiedbyeachphaseusingthemixingrule.
4:Theinfluenceoftexture.Singlecrystalsorpolycrystalshavetexture,whichleadstodifferencesintheatomicarrangementdensityofthecrystalsineachcrystaldirection,resultinginthermalexpansionanisotropy.Thethermalexpansioncoefficientparalleltothemainaxisofthecrystalislarge,andthethermalexpansioncoefficientissmallintheverticaldirection.
5:Internalcracksanddefectswillalsoaffectthethermalexpansioncoefficient.
