Výklad významu slova
Federalgovernmentreferstothecentralgovernmentofafederalcountry.Thefederalgovernmentusuallyappearsindemocraticcountriesundertheruleoflaw,orincountrieswithstronglocalawareness.Incontrasttocentralization,federalismisasystemofdecentralization.Itsconstitutiondividesmostgovernmentpowerstolocalgovernments.Thecentralgovernmentcanonlyberesponsibleforlimitedaffairs.Financialpower.Thefirstlevelofgovernmentiscalledthefederalgovernment,whichisthecentralgovernmentacrossthecountry.Thesecondlevelofgovernmentisthestategovernment,whichisanintegralpartofthefederalgovernment.
Formofkompozice
IntheUnitedStates,thefederationiscomposedofvariousstates.Asalocalcomponentofthecountry,the"state"canonlybeusedinthenameofacertainstateintheinternationalcommunity.Activity.IfacertainstateintheUnitedStateswantstosecedefromtheUnion,thefederalgovernmentwilldefinitelyintervene,andtheinternationalcommunitywillnotrecognizeitsnationalstatus.UnlesstheUSfederalgovernmentitselfrecognizesit,theinternationalcommunitywillbeabletorecognizeitsqualificationsasasubjectofinternationallawafteritsrecognition.IntheformerYugoslavia,thecountryconsistsofseveralcountriesformingafederation.Eachcountryhasitsownconstitutionanditsownnationalautonomy.Theyuniteonlytobetterfightforrightsintheinternationalcommunity.Recently,thetwofederalentitiesofSerbiaandMontenegro(SerbiaandMontenegroforshort)split,andeachbecameindependentastheRepublicofSerbiaandMontenegro,whichwasrecognizedbytheinternationalcommunity.
Systemform
Unitární systém
Thenationalstructureformofthegeneraladministrativeregionorautonomousregiondividedbyregionastheconstituentunit.Contrastwithcompoundsystem.Inaunitarycountry,thecentralgovernmentenjoysthehighestauthority,andthelocalgovernmentexercisesitspowersundertheunifiedleadershipofthecentralgovernmentandwithinthescopeofauthorityprescribedbytheconstitutionandlaws.Legally,allpowerinaunitarycountrybelongstothecentralgovernment,andlocalpowerisauthorizedbythecentralgovernment.Theobviousexternalcharacteristicsofaunitarycountryare:thecountryhasonlyonecentralpower,oneconstitution,andonelegalsystem.Itisthesubjectofinternationalrelationsininternationalexchanges,anditscitizenshaveonlyonenationality.Thisformisadoptedbymostmoderncountries.Accordingtothesizeoflocalauthority,unitarycountriescanbedividedintocentralizedunitarycountriesanddecentralizedunitarycountries.Inacentralizedandunitarycountry,thelocalgovernmentexercisesitspowersunderthestrictcontrolofthecentralgovernment.Officialsappointedbythecentralgovernmentorofficialselectedbythelocalgovernmentmanagelocaladministrativeaffairsonbehalfofthecentralgovernment.Localresidentshavenoautonomyorthelocalgovernmenthasautonomousagencies.,Buttheorgansofself-governmentarestrictlycontrolledbythecentralgovernment.Franceisatypicalcentralizedunitarycountry.Inacountrywithadecentralizedunitysystem,localresidentsindependentlyorganizelocalpublicagenciesinaccordancewiththelawandindependentlyhandlelocalaffairsunderthesupervisionofthecentralgovernment.Thecentralgovernmentshallnotinterfereinspecificlocalaffairs.Britainisatypicaldecentralizedunitarycountry.
Kompozitní systém
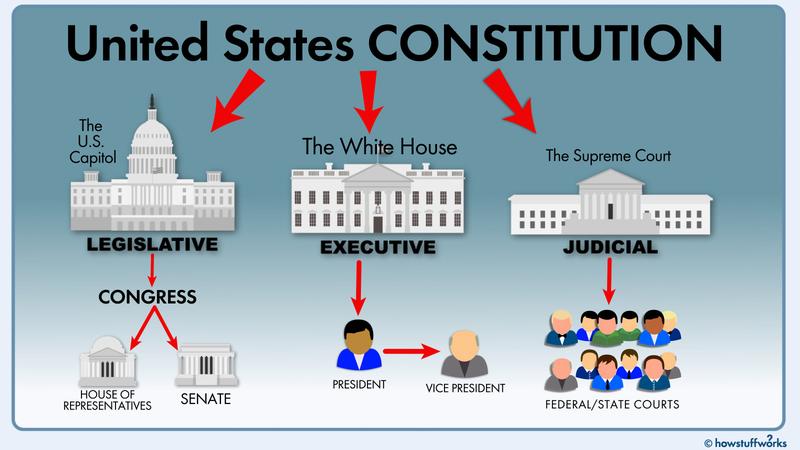
Kompozitní systém(symmetryofunitarysystem).Aformofnationalstructureinwhichseveralcountries(states,states,republics,etc.)unitethroughagreementstoformvariousnationalalliances.Acountrythatimplementsacompositesystemisacompositecountry.Therearefederal,confederateandotherforms.)Themainformofthestatestructure.Aformofnationalstructurewithacompletepoliticalentitythatenjoysrelativesovereigntyasitsconstituentunit.Inafederalstate,therelationshipbetweenthecountryasawholeanditsconstituentpartsisnottherelationshipbetweenthecentralandlocalgovernments,buttherelationshipbetweenthecentralandcentralgovernmentswithdifferentjurisdictions.ThescopeofauthorityofthecountryasawholeanditsconstituentpartsisstipulatedbytheFederalConstitution.Theyeachhavethehighestauthoritywithinthestipulatedscopeofauthority,andtheyaredirectlyexercisedbythepeoplewithoutanyinterferencewitheachother.Theobviousexternalcharacteristicsoffederalcountriesare:inadditiontothefederalgovernment,eachcomponentalsohasitsowncentralgovernment;thefederallegislatureusuallyhasachambercomposedofrepresentativesofthefederalcomponents;inadditiontothefederalconstitutionandthefederallegalsystem,EachcomponentoftheFederationalsohasitsownconstitutionandlegalsystem.Insomefederalcountries,itscomponentscanbecomethemainbodyofinternationalcommunicationoncertainissues;citizensoffederalcountrieshaveaunifiednationality.
TheUnitedStatesofAmericaisatypicalfederalsystem,andcountriessuchasKanada,Austrálie,andŠvýcarskoalsoadoptafederalsystem.TheUnitedStates,Russia,Německo,India,Brazil,andMexicoarefederalstates,whiletheformerSovietUnion,BosniaandHerzegovina(BosniaandHerzegovina),andtheoriginalCzechoslovakiaarefederalstates.
Ruská Federace
OnMay13,2000,RussianPresidentVladimirPutinsignedadecreetounite89entitiesoftheRuská Federace(republics,territories,andregions)into7ThepurposeoftheRuská Federace’sjurisdictionistoconsolidatenationalunityandstrengthenthepresident’slocalmanagementsystem.Thesevenfederaldistrictsare:theCentralDistrictwithMoscowasthecenter,theNorthwestDistrictwithSt.Petersburgasthecenter,theNorthCaucasusDistrictwiththeDonRostovasthecenter(laterchangedtotheSouthernDistrict),andthefollowingNovgorodTheareaalongtheVolgaRiverasthecenter,theUralareawithYekaterinburgasthecenter,theSiberiaareawithNovosibirskasthecenter,andtheFarEastareawithKhabarovskasthecenter.(Note:Thecenterofeachfederaldistrictisinbrackets)
CentralFederal District (Moskva)
Pobřeží Volhy Federální okres (Nižnij Novgorod)
Severozápadní federální okres (Petrohrad):
UralFederal District (Jekatěrinburg)
Sibiřský federální okres (Novosibirsk)
Severní Kavkaz Federální okres (Rostow-on-DonHusband)
TheRuská Federaceisnowcomposedof85federalsubjects:
(1) 22REPUBLIKY: Adygea (Adygea), AltairePublic, BashKortostanrepublic, Buryatia, Dagestan, Ingushetia, Kabarno-Balkaria, Kalmykia-Halimgetangechia, republice (republikán, republiku (republikán, republiku (republikán, republiku, republiku, republiku, republiku, republice. Republic of Tuva, Udmur Republic of Korea, Republic of Khakassia, Republic of Chechnya, Republic of Chuvash-Chavash, Republic of Crimea·;
(2)9 Kraj: Altajský kraj,Krasnodarské území,Krasnojarské území,Primorské území,Stavropolské území,Khabarovské území,Permské území,Kamčatské území,Transbajkalské území
(3)46 států:Amur,Arkhangelsk,Astrachaň,Belgorod,Brjansk,Vladimir,Volgograd,VologdaOblast,Voronežský oblast,Ivanovooblast,IrkutskOblast,KaliningradOblast,OrodiOblast,OrodiOblast,KirovOblast,Mostroma,Oblast,Kurgoblast,KurgangaOblast,KurgangaOblast ,NovosibirskOblast,OmskOblast,OrenburgOblast,OrelOblast,PenzaOblast,PskovOblast,RostovOblast,RyazanOblast,SamaraOblast,SaratovOblast,SakhalinOblast,SverdlovskOblast,SmolenskOblast,TambovOblast,SpecialVilOblast,TomskOblast,TulaOblast,TyumenOblast,UlyanovskOblast,ChelyabinskOblast,YaroslavlOblast,LipetskOblast,KemerovoOblast;
(4)3 federální obce: Moskva, Petrohrad a Sevastopol;
(5)1autonomní region:Židovský autonomní region;
(6)4 autonomní regiony: autonomní region Něnec, autonomní region Čukotka, autonomní region Jamal-Nenet, autonomní region Chanty-Mansi.
Americký systém
Země je rozdělena do 10 regionů, 50 států a 1 DC (Washington, District of Columbia). Existuje 3042 hrabství nebo hrabství (hrabství, hrabství Louisiana) Isparish)
Regiony:Nová Anglie,Střední,Střední Atlantik,Jihozápad,Apalačský region,Alpský,Jihovýchodní,Pacifik,Velká jezera,Aljaška a Havajské státy,Alabama,Aljaška,Arizona,Arkansas,Kalifornie,Colorado,Connecticut,Holaware,HawaiorginoIs Indiana,Iowa,Kansas,Kentucky,Louisiana,Maine,Maryland,Massachusetts,Michigan,Minnesota,Mississippi,Missouri,Montana,Nebraska,Nevada,NewHampshire,NewJersey,NewMexico,NewYork,Severní Karolína,Pharma,Oklahoska,Okla RhodeIsland, Jižní Karolína, Jižní Dakota, Tennessee, Texas, Utah, Vermont, Virginie, Washington, Západní Virginie, Wisconsin, Wyoming;
Federální území
PuertoRicoCommonwealthandNorthernMariana;
Zámořská území
(obydleno):Americká Samoa,Guam,MidwayIsland,U.S.Virgin Islands;
(neobydlený): BakerIsland, Howland Island, Jarvis Island, Johnston Island, KingmanReef, Navassa Island, Palmer Island, Wake Island.
Kanada
TheCanadianParliamentBuildingKanadaisdividedintotenprovincesandthreeregions.Theprovincehasconsiderableautonomyfromthefederalgovernment,whilethespecialzonehasless.
Federální vláda Kanady
Eachprovinceandterritoryhasasingle-chamberassembly.
Alberta (anglicky, francouzsky: Alberta, rok založení: 1905, hlavní město: Edmonton)
BritishColumbia (anglicky:BritishColumbia,francouzsky:Colombie-Britannique,Jiný rok:1871,hlavní město:Victoria)
Manitoba (anglicky, francouzsky: Manitoba, rok připojení 1870, hlavní město: Winnipeg)
NewfoundlandaLatinská AmerikaBrado(anglicky:NewfoundlandandLabrador,francouzsky:Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador,rok spojení:1949,hlavní město:St.John's)
NewBrunswick (anglicky:NewBrunswick,francouzsky:Nouveau-Brunswick,rok připojení:1867,hlavní město:Federicton)
Severozápad (angličtina:NorthwestTerritories,francouzština:TerritoiresduNord-Ouest,rok připojení:1870,hlavní město:Yellowknife)
NovaScotia(anglicky:NovaScotia,francouzsky:Nouvelle-Écosse,rok připojení:1867,hlavní město:Halifax)
Nunavut(angličtina,francouzština:Nunavut,oddělená od Severozápadních území v roce 1999,hlavní město:Iqaluit)
Ontario (anglicky, francouzsky: Ontario, rok připojení: 1867, hlavní město: Toronto)
PrinceEdwardIsland(anglicky:PrinceEdwardIsland,francouzsky:Île-du-Prince-Édouard,rok spojení:1873,hlavní město:Charlottetown)
Québec(francouzsky:Québec,anglicky:Quebec,rok spojení:1867,hlavní město:QuebecCity)
Saskatchewan (anglicky, francouzsky: Saskatchewan, rok založení: 1905, hlavní město: Regina)
Yukon(anglicky,francouzsky:YukonTerritory,připojenýrok:1898,hlavní město:Whitehorse)
Ostatní země
Německo
Rakousko
Švýcarsko
Austrálie
